Introducing HP-UX Mobile IPv6
9
2.3.3 Return Routability Procedure
Most Mobile Nodes use Route Optimization after they receive a data packet from a Correspondent
Node through the Home Agent, thereby indicating the Correspondent Node does not have binding
information with the Mobile Node’s current Care-of Address. To establish Route Optimization, the
Mobile Node sends a Binding Update message to the Correspondent Node with its current Care-of
Address. To prevent attackers from sending false Binding Update messages, the Binding Update is
authenticated using a cryptographic signature that verifies the Correspondent Node can contact the
Mobile Node using both its Home Address and the proposed Care-of Address. Verifying that the
Correspondent Node can contact the Mobile Node using both addresses is known as the return
routability procedure.
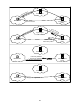
The following list explains the steps for the return routability procedure, which is shown in the figure on
the following page:
1. The Mobile Node sends a Care-of Test Init message and a Home Test Init message to the
Correspondent Node.
2. The Correspondent Node sends Care-of Test and Home Test responses to the Mobile Node.
3. The Mobile Node calculates a binding management key (Kbm) from the Care-of Test and Home Test
messages.
4. The Mobile Node sends an authenticated Binding Update message to the Correspondent Node with
its Care-of Address.
5. The Correspondent Node verifies the Binding Update message and sends a Binding Acknowledgment
(Note: This step not shown in graphic).