HP-UX Mobile IPv6 A.01.00 Administrator's Guide
Chapter 1
Introducing HP-UX Mobile IPv6
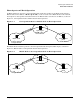
Mobile IPv6 Architecture
4
Mobile IPv6 Architecture
IPv6 addresses are topologically correct, therefore nodes attached to the same physical network or LAN
segment must have the same IPv6 network address prefix. Mobile IPv6 provides transparent routing of IP
data-packets to a mobile IP device or node, such as a portable computer, regardless of the mobile node’s point
of attachment to the network. Mobile IPv6 allows a mobile node to move from one wireless access point or
base station with no disruption in network connectivity.
The main components of Mobile IPv6 operation are:
• Mobile Node
• Home Address
• Care-of Address
• Correspondent Node
• Home Agent (for basic operation)
• Route Optimization
Mobile Node and Home Address
With Mobile IPv6, a client IP node, or Mobile Node (MN), can change network attachment points and use a
single, fixed IPv6 address for extended periods of time, regardless of its current attachment point. This
address is known as the Mobile Node’s home address. Without Mobile IPv6, Mobile Nodes cannot use a
single, fixed IPv6 address while they roam. Instead, each time a Mobile Node moves and changes network
attachment points, it must manually re-configure a new IP address and default router based on its current
location—temporarily losing its network connections and ability to communicate in the process.
The Mobile Node’s home address is a unicast routable (global) address, with the network prefix of the Mobile
Node’s home network. The Mobile Node’s home network is the network that administers the Mobile Node,
and is typically the network to which the Mobile Node is normally attached.
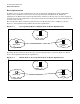
Care-of Address
When a Mobile Node is attached to a foreign network (a network other than its home network), it gets a
temporary Care-of Address (COA) on the foreign network. The Care-of Address is an IPv6 unicast global
address with the network prefix of the foreign network. The Mobile Node can get this address using IPv6
stateless auto-configuration, or by using a stateful configuration method (such as DHCP).
Correspondent Nodes
In Mobile IPv6 architecture, a node that communicates or corresponds with the Mobile Node is referred to as
a Correspondent Node (CN).
NOTE The same server can be both a Home Agent and a Correspondent Node.