HP-UX IPv6 Transport Administrator Guide HP-UX 11i v3 (5992-6426, May 2013)
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX IPv6 Transport Administrator Guide
- Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Features Overview
- IPv6 Transport
- New IPv6 Transport Features
- Support for RFC 3542 (Advanced Sockets API for IPv6)
- Configurable Policy Table Support
- Anycast Address Support
- Support for RFC 4291 (IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture)
- Support for RFC 4213 (Basic Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers)
- Support for RFC 3484 (Default Address Selection for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6))
- Support for RFC 3493 (Basic Socket Interface Extensions for IPv6)
- Support for RFC 4584 (Extension to Sockets API for Mobile IPv6)
- Support for RFC 4193 (Unique Local IPv6 Unicast Addresses)
- Support for RFC 4443 (Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6 (ICMPv6))
- Support for IPv6 over VLAN
- Ability to Disable Autoconfiguration Based on Router Advertisements
- Support for RFC 3810 (Multicast Listener Discovery Version 2 (MLDv2))
- Support for RFC 3376 (Internet Group Management Protocol Version 3 (IGMPv3))
- Support for RFC 3678 (Socket Extension to Multicast Source Filter API)
- Support for RFC 4941 (Privacy Extensions for Stateless Address Autoconfiguration in IPv6)
- New ndd Tunables
- IPv6 Transport Features Available in the Core HP-UX 11i v3 Operating System
- Limitations
- IPv6 Transport
- 2 Configuration
- Configuring IPv6 Interfaces and Addresses
- Stateless Autoconfiguration
- Manual Configuration
- Configurable Policy Table for Default Address Selection for IPv6
- Host Names and IPv6 Addresses
- 3 Troubleshooting
- 4 IPv6 Addressing and Concepts
- 5 IPv6 Software and Interface Technology
- 6 Utilities
- A IPv6 ndd Tunable Parameters
- Index
NOTE: Refer to the ifconfig(1m) man page and the
/etc/rc.config.d/netfconf-ipv6 file for more detailed information on tunneling
parameters.
“6to4” - Connecting IPv6 Domains over IPv4 Clouds
“6to4” is an automatic tunneling mechanism that can be used to provide connectivity
between isolated IPv6 domains or hosts across an IPv4 infrastructure and with native
IPv6 domains via relay routers. “6to4” is based on the IP6-in-IP tunneling mechanism
defined in RFC 2893 and it falls under the router-to-router tunneling scenario.
“6to4” uses the concept of automatic tunneling where the tunnel end-point is determined
from the IPv6 destination address and avoids the complexity of manual tunnel
configuration. It does not use the IPv4-compatible address, but instead determines the
tunnel endpoint IPv4 address from the special “6to4” prefix of the IPv6 destination
address.
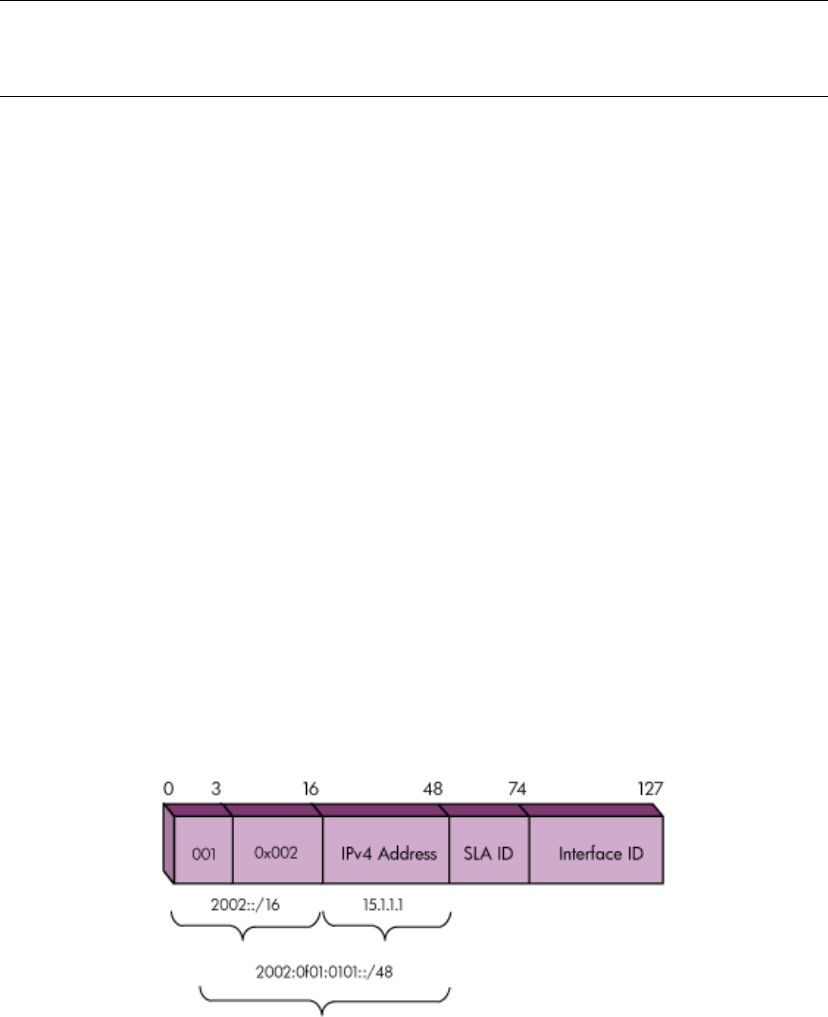
“6to4” Well-Known Prefix
“6to4” defines an address assignment scheme that allows a site to obtain a unique
externally routable prefix if the site has at least one globally unique IPv4 address. The
Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) has assigned the unique IPv6 address prefix
of 2002::/16 for “6to4”. Each site must have a border dual stack router that has at
least one global IPv4 address.
A “6to4” prefix can be generated by concatenating the 2002:: prefix to the global
IPv4 address. For example, if the dual stack router has an IPv4 address 15.1.1.1, then
its “6to4” prefix will be 2002:0f01:0101::/48. The “6to4” prefix provides a network
prefix for the local IPv6 host or network. The IPv4 address is the endpoint for all external
IPv4 connections.
Figure 12 “6to4” Prefix
“6to4” Encapsulation
IPv6 packets from a “6to4” site are encapsulated in IPv4 packets when they leave the
site over its external IPv4 connection. IPv6 packets are transmitted in IPv4 packets with
Migrating from IPv4 to IPv6 59










