HP-UX IPv6 Transport Administrator Guide HP-UX 11i v3 (5992-6426, May 2013)
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX IPv6 Transport Administrator Guide
- Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Features Overview
- IPv6 Transport
- New IPv6 Transport Features
- Support for RFC 3542 (Advanced Sockets API for IPv6)
- Configurable Policy Table Support
- Anycast Address Support
- Support for RFC 4291 (IP Version 6 Addressing Architecture)
- Support for RFC 4213 (Basic Transition Mechanisms for IPv6 Hosts and Routers)
- Support for RFC 3484 (Default Address Selection for Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6))
- Support for RFC 3493 (Basic Socket Interface Extensions for IPv6)
- Support for RFC 4584 (Extension to Sockets API for Mobile IPv6)
- Support for RFC 4193 (Unique Local IPv6 Unicast Addresses)
- Support for RFC 4443 (Internet Control Message Protocol for IPv6 (ICMPv6))
- Support for IPv6 over VLAN
- Ability to Disable Autoconfiguration Based on Router Advertisements
- Support for RFC 3810 (Multicast Listener Discovery Version 2 (MLDv2))
- Support for RFC 3376 (Internet Group Management Protocol Version 3 (IGMPv3))
- Support for RFC 3678 (Socket Extension to Multicast Source Filter API)
- Support for RFC 4941 (Privacy Extensions for Stateless Address Autoconfiguration in IPv6)
- New ndd Tunables
- IPv6 Transport Features Available in the Core HP-UX 11i v3 Operating System
- Limitations
- IPv6 Transport
- 2 Configuration
- Configuring IPv6 Interfaces and Addresses
- Stateless Autoconfiguration
- Manual Configuration
- Configurable Policy Table for Default Address Selection for IPv6
- Host Names and IPv6 Addresses
- 3 Troubleshooting
- 4 IPv6 Addressing and Concepts
- 5 IPv6 Software and Interface Technology
- 6 Utilities
- A IPv6 ndd Tunable Parameters
- Index
Where <IPv6-Node-Address> is an IPv6 address and <Prefix-Length> is a
decimal value specifying how many of the leftmost contiguous bits of the address compose
the subnet prefix.
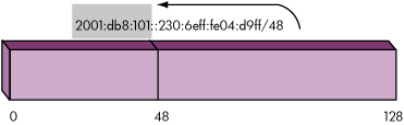
In Figure 8, prefix length 48 specifies that the leftmost 48 bits of the IPv6 address compose
the subnet prefix.
Figure 8 Example Prefix Length 48
Address Scope
Link-local An IPv6 addres s used on a single link.
Global An IPv6 address that uniquely identifies a node on the Internet such
that packets can be routed to the node from any other node on the
Internet.
Address Type
Unicast Identifies a single interface. Notable unicast addresses are:
Loopback ::1 Address internal to IPv6 stack
Unspecified :: Not a legally defined address
Anycast Identifies a group of interfaces, possibly belonging to different nodes. A
packet sent to an anycast address is delivered to only one of the interfaces
in the group.
Multicast Identifies a group of interfaces, possibly belonging to different nodes. A
packet sent to a multicast address is delivered to all the interfaces in this
group.
Neighbor Discovery
IPv6 hosts and routers use the IPv6 Neighbor Discovery Protocol to:
• advertise their link-layer address on the local link
• find neighbors’ link-layer addresses on the local link
• find neighboring routers able to forward IPv6 packets
• actively track which neighbors are reachable
• search for alternate routers when a path to a router fails
Neighbor Discovery 47










