HP-UX IPv6 Transition Mechanisms White Paper
6
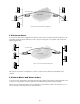
IPv4 network
IP6-in-IP tunnel
IPv4 Router
IPv6/IPv4 Router
Figure 4: router-to-host tunnel configuration
IPv4 host
IPv4 host
IPv6/IPv4 host
IPv6 host
IPv6 host
6. 6to4
6to4 is an automatic router-to-router tunneling mechanism that can be used to provide connectivity
between isolated IPv6 sites or hosts across the IPv4 infrastructure and with IPv6-only sites via relay
routers. Each 6to4 site should have a site border 6to4 (dual stack) router, which is one endpoint of the
6to4 automatic tunnel.
6to4 further defines an address assignment scheme that allows a site to obtain an unique externally
routable prefix if the site has at least one globally unique IPv4 address. The Internet Assigned Number
Authority has assigned the unique prefix 2002::/16 for 6to4 mechanism. The site border dual stack
router should have at least one global IPv4 address, a 6to4 prefix can be generated by concatenating
the 2002:: prefix to the global IPv4 address. For example, if the dual stack router has an IPv4 address
15.13.136.1, then its 6to4 prefix will be 2002:0f0d:8801::/48. The embedded IPv4 address will be
used as the tunnel endpoint address by the 6to4 mechanism.
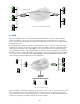
IPv4 network
6to4 host
6to4 router
6to4 relay router
6to4 host
6to4 router
6to4 host6to4 host
Figure 5: 6to4 network topology
IPv6 host
IPv6 host
IPv6 host
Figure 5 illustrates a 6to4 network topology. 6to4 topology consists of one or more 6to4 hosts in a 6to4
site, a 6to4 border router on the site that has at least one IPv4 connection to the Internet and a 6to4
relay router that is used to connect to native IPv6 site. A 6to4 relay router is different from a 6to4 router
in that it has a 6to4 pseudo interface and at least one IPv6 interface.