HP-UX IPv6 Porting Guide (September 2004)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction
- 2 IPv6 Addressing
- 3 Data Structure Changes
- 4 Migrating Applications from IPv4 to IPv6
- 5 Overview of IPv4 and IPv6 Call Set-up
- 6 Function Calls Converting Names to Addresses
- 7 Function Calls Converting IP addresses to Names
- 8 Reading Error Messages
- 9 Freeing Memory
- 10 Converting Binary and Text Addresses
- 11 Testing for Scope and Type of IPv6 addresses using Macros
- 12 Identifying Local Interface Names and Indexes
- 13 Configuring or Querying an Interface using IPv6 ioctl() Function Calls
- 14 Verifying IPv6 Installation
- 15 Sample Client/Server Programs
- A IPv4 to IPv6 Quick Reference Guide
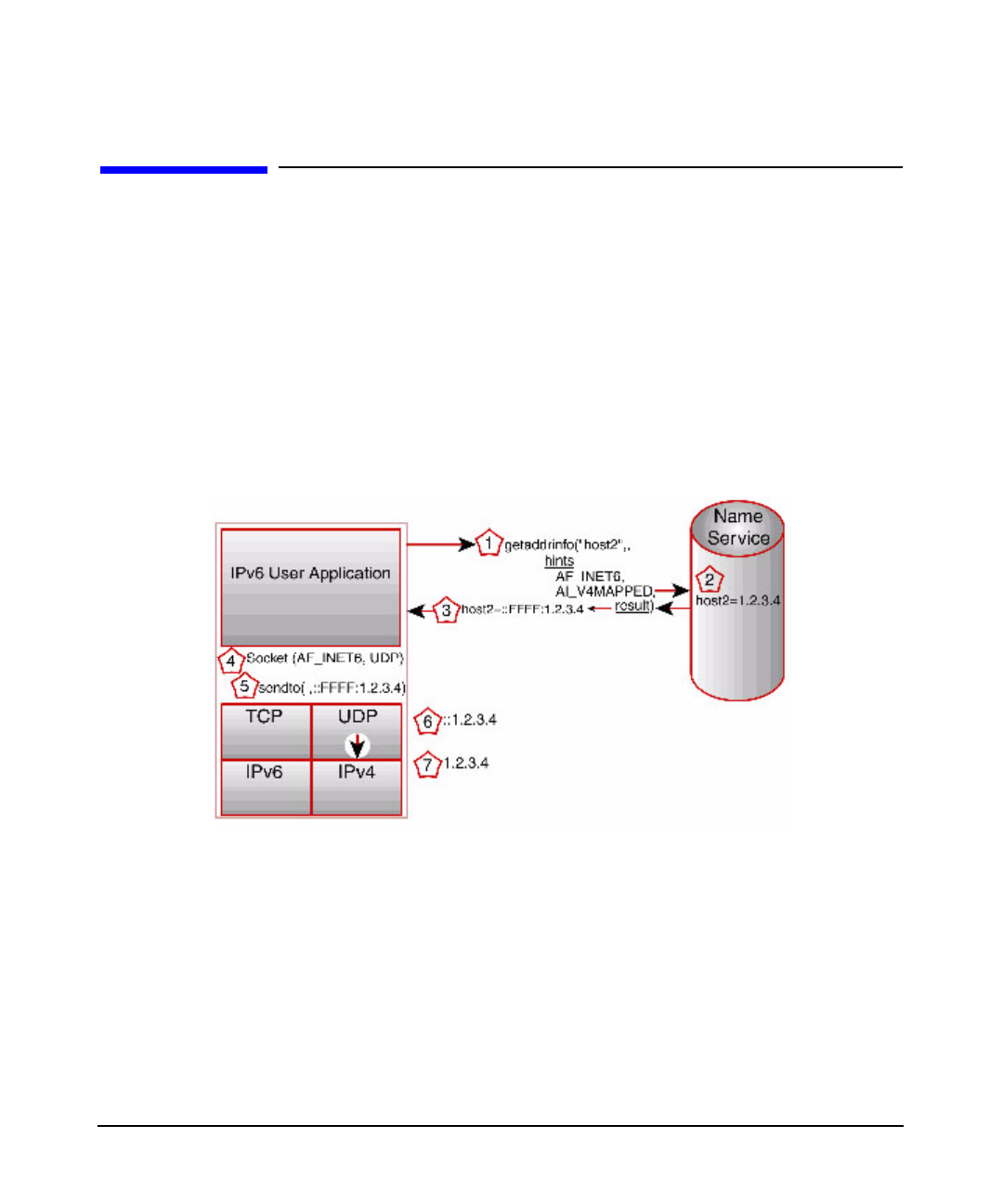
Overview of IPv4 and IPv6 Call Set-up
Using AF_INET6 Socket to Send IPv4 UDP Communications
Chapter 5 25
Using AF_INET6 Socket to Send IPv4 UDP
Communications
You can use the AF_INET6 socket for both IPv6 and IPv4 communications; IPv6 uses the
POSIX function call getaddrinfo() rather than the IPv4 gethostbyname() function call. For
IPv4 communications, create an AF_INET6 socket and pass it a sockaddr_in6 structure that
contains an IPv4-mapped IPv6 address (for example, ::FFFF:1.2.3.4). The figure below
shows the sequence of events for an application that uses an AF_INET6 socket to send IPv4
packets.
Figure 5-2
1. Application calls getaddrinfo() and passes:
• the host name (host2).
• the AF_INET6 address family
hint
, which asks the Name Service for an IPv6 address
corresponding to the host name.
• The AI_V4MAPPED
flag hint
, which tells the function that if the Name Service finds
no IPv6 address but finds an IPv4 address for host2, return the IPv4 address within
an IPv4-mapped IPv6 address. See getaddrinfo(3N) later in this document for a
description of
hints
and
flags
values.










