HP-UX IPv6 Porting Guide (September 2004)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction
- 2 IPv6 Addressing
- 3 Data Structure Changes
- 4 Migrating Applications from IPv4 to IPv6
- 5 Overview of IPv4 and IPv6 Call Set-up
- 6 Function Calls Converting Names to Addresses
- 7 Function Calls Converting IP addresses to Names
- 8 Reading Error Messages
- 9 Freeing Memory
- 10 Converting Binary and Text Addresses
- 11 Testing for Scope and Type of IPv6 addresses using Macros
- 12 Identifying Local Interface Names and Indexes
- 13 Configuring or Querying an Interface using IPv6 ioctl() Function Calls
- 14 Verifying IPv6 Installation
- 15 Sample Client/Server Programs
- A IPv4 to IPv6 Quick Reference Guide
IPv6 Addressing
Types of IPv6 addresses
Chapter 26
Types of IPv6 addresses
IPv6 supports both single-destination (unicast) and multiple-destination (multicast)
addresses. Addresses comprise three different scopes.
IPv4 to IPv6 Transition Addresses
To ease the transition from IPv4 to IPv6, the IPv6 Protocol Specifications define two global
IPv6 addresses containing unique IPv4 address in the low-order 32-bits of the IPv6 address.
IPv6 Address scope
Link-local: An IPv6 address used over one local link; assigned during autoconfiguration.
Site-local: An IPv6 address used inside a local Intranet site only; not renumbered by an ISP.
Global: An IPv6 address used throughout the Internet.
An IPv6 node always has a link-local address. It may have a site-local address or one or more
global addresses.
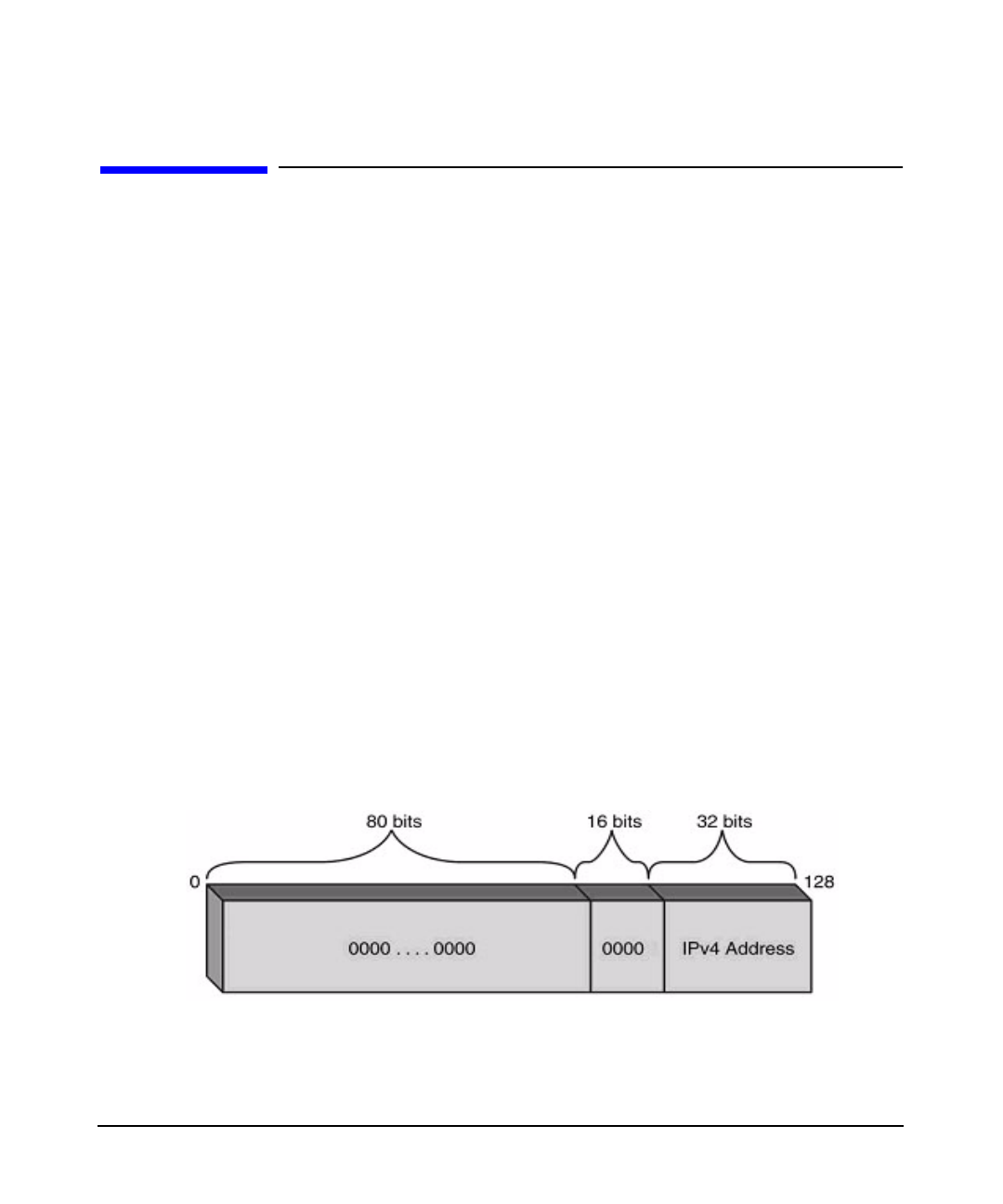
IPv4-Compatible IPv6 Address
An administrator assigns an IPv4-compatible IPv6 address and host name entry to the Name
Service for an IPv4/IPv6 host where no IPv6 router is available.The IPv4-compatible IPv6
address is an IPv6 address in the format:
Figure 2-1 IPv4-Compatible Address
IPv4-Compatible Addresses help the migration process by enabling IPv6 features without
requiring IPv6 Routers.










