HP-UX IPSec Version A.03.02.02 Administrator's Guide HP-UX 11i version 2 and HP-UX 11i version 3 (762800-001, April 2014)
◦ Configuration test utility
The ipsec_policy utility takes a packet definition (local and remote IP addresses,
upper-layer protocol, local and remote port numbers) as input and reports the IPsec policy
that HP-UX IPSec would apply to packets matching the definition.
◦ Audit logging
HP-UX IPSec maintains an audit log of events, including events that may indicate attempts
to compromise network security.
◦ Data reporting utility
The ipsec_report utility reports IPsec runtime data, including information about security
associations or sessions, and entries in the audit log.
◦ Status reporting utility
The ipsec_admin utility reports the status of HP-UX IPSec components. The ipsec_admin
utility also performs general administrative functions, such as starting and stopping HP-UX
IPSec, setting the audit level, and deleting or resetting runtime data.
IPsec protocol suite
The major components of the IPsec protocol suite can be divided into the following categories:
• Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) header for data confidentiality, data integrity, and data
authentication. The ESP header also includes a sequence number that provides a form of
replay protection.
• Authentication Header (AH) for data integrity and authentication. The AH header also includes
a sequence number for a form of replay protection.
• Internet Key Exchange (IKE) protocol, for generating and distributing cryptography keys for
ESP and AH. IKE also authenticates the identity of the remote system, so AH and authenticated
ESP with IKE keys provides data origin authentication.
• Manual Keys, an alternative to IKE. Instead of dynamically generating and distributing
cryptography keys for ESP and AH, the cryptography keys are static and manually distributed.
Manual keys are typically used only when the remote system does not support IKE.
Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP)
The IPsec Encapsulating Security Payload (ESP) uses shared key encryption to provide data privacy
and shared key hash functions to provide data authentication and data integrity.
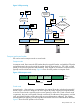
Shared key encryption
In shared key encryption, two parties know the same cryptographic key. The sender (System A in
Figure 1) encrypts the data with the key to create encrypted data. The recipient (System B in
Figure 1) decrypts the encrypted data with the same key. Since only a holder of the cryptographic
key can decrypt the data, the encrypted data can be transmitted across the network without being
understood by other parties.
32 HP-UX IPSec overview