HP-UX IPSec version A.02.01 Administrator's Guide
HP-UX IPSec Overview
IPsec Protocol Suite
Chapter 1 39
used. This makes it difficult for a third party to intercept a message and
replace it with a new message that generates the same authentication
code. This ensures that only a holder of the secret key can generate the
correct authentication code.
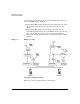
In Figure 1-2, the sender, System A, uses the plaintext (data) and the
shared key to calculate an HMAC for the data and sends the HMAC with
the data. The recipient, System B, computes its own HMAC value using
the same shared secret key and data. The recipient then compares the
result with the transmitted HMAC. If the HMAC values match, the
recipient is assured that the sender knows the same secret key,
confirming the identity of the sender. The recipient is also assured that
the data was not altered during transit.
Figure 1-2 Shared Key Hash Function
ESP Processing
On the sender (System A), the ESP module processes the outbound
packet as follows:
1. The ESP module encrypts the IP payload using the encryption key
(KeyE.
2. The ESP module collates an authentication value (the HMAC), for
the encrypted payload using the authentication key (KeyA) and
appends the authentication value to the packet.