HP-UX IPSec version A.02.01 Administrator's Guide
HP-UX IPSec Overview
IPsec Protocol Suite
Chapter 138
cryptographic key can decrypt the data, the encrypted data can be
transmitted across the network without being understood by other
parties.
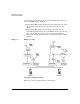
Figure 1-1 Shared Key Encryption
Shared key cryptography alone does not provide protection against
tampering. An intruder can still intercept encrypted data and alter it
before sending it to the correct destination. For this reason, ESP also
authenticates the encrypted data.
Shared key cryptography is also referred to as symmetric key
cryptography (because the keys used by both parties must be the same)
and private key cryptography (because the two parties must keep the
key private).
Shared Key Hash Functions
Shared key hash functions (also known as a symmetric key hash
functions) are hash functions that take a large block of variable-length
data and a shared key as input and produce a small, fixed-length hash
value, or authentication code. The IPsec protocol suite uses a specific
method for producing the hash value and refers to the authentication
value as the Hashed Message Authentication Code (HMAC).
Shared keyed hash functions are usually based on one-way hash
functions: Starting with a hash output value, it is difficult to create an
input value that would generate the same output value, even if no key is