HP-UX IPSec vA.03.00 Performance and Sizing White Paper
Table Of Contents
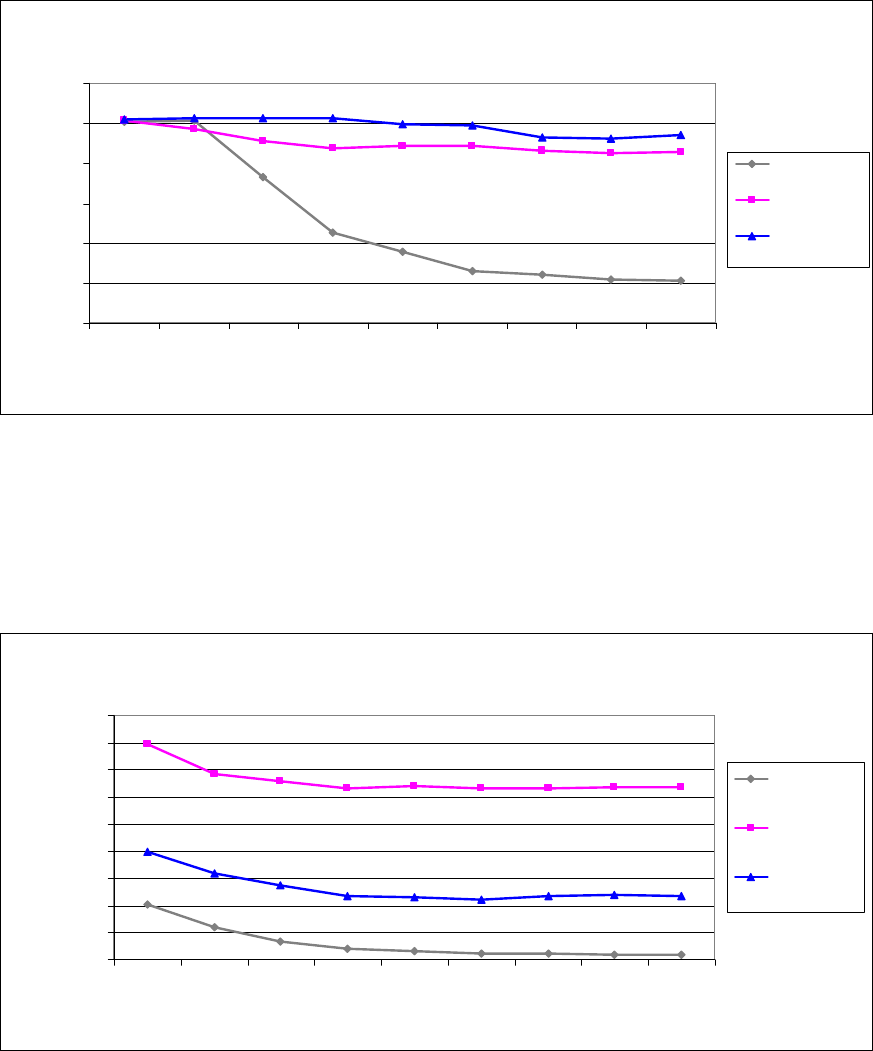
CPU utilization
Figure 5 shows the percentage of the CPU used by the sending system. CPU utilization for ESP-AES-
HMA
C-SHA1 is lower than CPU utilization for ESP-3DES-HMAC-SHA1, even though ESP-AES-HMAC-
SHA1 provides the strongest encryption and better throughput rate.
Figure 5. Single dual-core (2-way) CPU utilization for raw IP, ESP-3DES-HMAC-SHA1, and ESP-AES-HMAC-SHA1
Single dual-core (2-way) CPU utilization
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
128 256 512 1024 2048 4096 8192 16384 32768
Message size (bytes)
Percentage (%)
Raw
ESP-3DES-
HMAC-SHA1
ESP-AES-
HMAC-SHA1
Service demand
Figure 6 shows the service demand levels for ESP-3DES-HMAC-SHA1 and ESP-AES-HMAC-SH
A1.
Lower service demand levels indicate greater efficiency. Other than raw data, the service demand
levels are lowest for ESP-AES-HMAC-SHA1.
Figure 6. Single dual-core (2-way) service demand rates for raw IP, ESP-3DES-HMAC-SHA1, and ESP-AES-HMAC-SHA1
Single dual-core (2-way) service demand
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
128 256 512 1024 2048 4096 8192 16384 32768
Message size (bytes)
Service demand
(microsec/KB)
Raw
ESP-3DES-
HMAC-SHA1
ESP-AES-
HMAC-SHA1
Security Association Measurements
You can use HP-UX IPSec with static, manually configured cryptography keys to encrypt and
authenticate data. However, most installations use HP-UX IPSec with the Internet Key Exchange (IKE)
protocol, which generates and manages dynamic keys for data encryption and authentication.
7










