HP-UX IPFilter A.03.05.13 Administrator's Guide: HP-UX 11i v3
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX IPFilter Version A.03.05.13 Administrator's Guide
- Legal Notices
- Table of Contents
- Preface: About This Document
- 1 Installing and Configuring HP-UX IPFilter
- Overview of HP-UX IPFilter Installation
- Step 1: Checking HP-UX IPFilter Installation Prerequisites
- Step 2: Loading HP-UX IPFilter Software
- Step 3: Determining the Rules for IPFilter
- Step 4: Adding Rules to the Rules Files
- Step 5: Loading IPFilter and NAT Rules
- Step 6: Verifying the Installation and Configuration
- Kernel Tunable Parameters
- Supported and Unsupported Interfaces
- Troubleshooting HP-UX IPFilter
- 2 HP-UX IPFilter on HP-UX 11i Version 3
- 3 Rules and Keywords
- IPFilter Configuration Files
- Basic Rules Processing
- IPFilter Keywords
- pass and block: Controlling IP Traffic
- in and out: Bidirectional Filtering
- quick: Optimizing IPFilter Rules Processing
- on: Filtering by Network Interfaces
- from and to: Filtering by IP Addresses and Subnets
- log: Tracking Packets on a System
- proto: Controlling Specific Protocols
- opt and ipopts: Filtering on IP Options
- icmp-type: Filtering ICMP Traffic by Type
- port: Filtering on TCP and UDP Ports
- keep state: Protecting TCP, UDP, and ICMP Sessions
- flags: Tight Filtering Based on TCP Header Flags
- keep frags: Letting Fragmented Packets Pass
- with frags: Dropping Fragmented Packets
- with short: Dropping Short Fragments
- return-rst: Responding to Blocked TCP Packets
- return-icmp: Responding to Blocked ICMP Packets
- dup-to: Drop-Safe Logging
- NAT Keywords
- 4 Dynamic Connection Allocation
- 5 Firewall Building Concepts
- Blocking Services by Port Number
- Using Keep State
- Using Keep State with UDP
- Using Keep State with ICMP
- Logging Techniques
- Improving Performance with Rule Groups
- Localhost Filtering
- Using the to
- Creating a Complete Filter by Interface
- Combining IP Address and Network Interface Filtering
- Using Bidirectional Filtering Capabilities
- Using port and proto to Create a Secure Filter
- 6 HP-UX IPFilter Utilities
- 7 HP-UX IPFilter and FTP
- 8 HP-UX IPFilter and RPC
- 9 HP-UX IPFilter and IPSec
- 10 HP-UX IPFilter and Serviceguard
- A HP-UX IPFilter Configuration Examples
- B HP-UX IPFilter Static Linking
- C Performance Guidelines
- Index
Rules and Keywords
IPFilter Keywords
Chapter 3 41
icmp-type: Filtering ICMP Traffic by Type
You can filter specific types of ICMP traffic using the icmp-type keyword.
This is a useful keyword if you want to block most ICMP traffic to
prevent DoS attacks, but must allow certain types of ICMP messages to
pass to your system.
For example if you want to specifically allow ping messages to pass on
your system, configure the following rule:
pass in quick on lan0 proto icmp from any to 20.20.20.0/24
icmp-type 0
You must know the type number for any ICMP message you want to
explicitly pass or block using the icmp-type keyword. The following is a
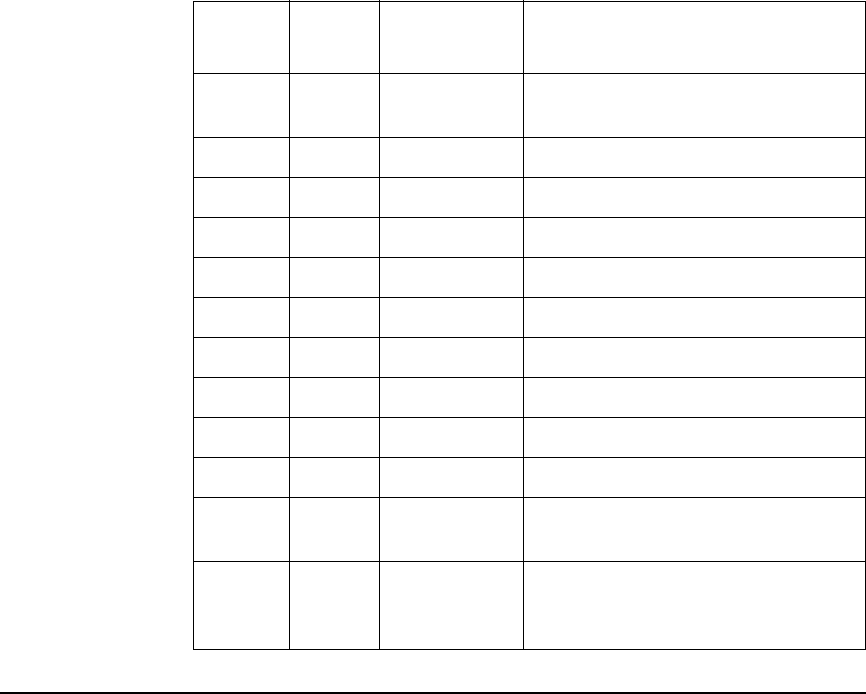
list of ICMP message type numbers used by HP-UX IPFilter.
TYPE CODE
icmp-type
icmp-code
MEANING
0 0 echorep ECHO REPLY (ping reply)
[RFC792]
3 unreach DESTINATION UNREACHABLE
0 net-unr network unreachable
1 host-unr host unreachable
2 proto-unr protocol unreachable
3 port-unr port unreachable [RFC792]
4 needfrag need fragmentation [RFC792]
5 srcfail source route failed [RFC792]
6 net-unk destination network unknown
7 host-unk destination host unknown
8 isolate source host isolated [RFC792]
(ping)
9 net-prohib destination network
administratively prohibited
[RFC1256]










