HP-UX Host Intrusion Detection System Version 4.3 administrator guide
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX Host Intrusion Detection System Version 4.3 administrator guide
- Table of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Configuring HP-UX HIDS
- 3 Getting Started with HP-UX HIDS
- 4 Using the System Manager Screen
- Starting the HP-UX HIDS System Manager
- Stopping the HP-UX HIDS System Manager
- System Manager Components
- Starting HP-UX HIDS Agents
- Getting the Status of Agent Hosts
- Resynchronizing Agent Hosts
- Activating Schedules on Agent Hosts
- Stopping Schedules on Agent Hosts
- Halting HP-UX HIDS Agents
- Accessing Other Screens
- 5 Using the Schedule Manager Screen
- The Schedule Manager
- Configuring Surveillance Schedules
- Configuring Surveillance Groups
- Configuring Detection Templates
- Setting Surveillance Schedule Timetables
- Configuring Alert Aggregation
- Configuring Monitor Failed Attempts
- Configuring Duplicate Alert Suppression
- Viewing Surveillance Schedule Details
- Predefined Surveillance Schedules and Groups
- 6 Using the Host Manager Screen
- 7 Using the Network Node Screen
- 8 Using the Preferences Screen
- A Templates and Alerts
- Alert Summary
- UNIX Regular Expressions
- Limitations
- Template Property Types
- Buffer Overflow Template
- Race Condition Template
- Modification of files/directories Template
- Changes to Log File Template
- Creation and Modification of setuid/setgid File Template
- Creation of World-Writable File Template
- Modification of Another User’s File Template
- Login/Logout Template
- Repeated Failed Logins Template
- Repeated Failed su Commands Template
- Log File Monitoring Template
- B Automated Response for Alerts
- C Tuning Schedules and Generating Alert Reports
- D The Agent Configuration File
- E The Surveillance Schedule Text File
- F Error Messages
- G Troubleshooting
- Troubleshooting
- Agent and System Manager cannot communicate with each other
- Agent complains that idds has not been enabled, yet lsdev shows /dev/idds is present
- Agent does not start on system boot
- Agent halts abnormally, leaving ids_* files and message queues
- Agent host appears to hang and/or you see message disk full
- Agent needs further troubleshooting
- Agent does not start after installation
- Agents appear to be stuck in polling status
- Agent displays error if hostname to IP mapping is not registered in name service
- Aggregated alerts targets or details field are truncated and the same aggregated alert has several entries logged in the IDS_ALERTFILE
- Alert date/time sort seems inconsistent
- Alerts are not being displayed in the alert browser
- Buffer overflow triggers false positives
- Duplicate alerts appear in System Manager
- Getting several aggregated alerts for the same process
- GUI runs out of memory after receiving around 19,000 alerts
- The idsadmin Command needs installed agent certificates
- The idsadmin Command notifies of bad certificate when pinging a remote agent
- IDS_checkInstall fails with a kmtune error
- IDS_genAdminKeys or IDS_genAgentCerts does not complete successfully
- IDS_genAdminKeys or idsgui quits early
- Large files in /var/opt/ids
- Log files are filling up
- No Agent Available
- Normal operation of an application generates heavy volume of alerts
- Reflection X rlogin produces multiple login and logout alerts
- Schedule Manager timetable screen appears to hang
- SSH does not perform a clean exit after idsagent is started
- System Manager appears to hang
- System Manager does not let you save files to specific directories
- System Manager does not start after idsgui is started
- System Manager starts with no borders or title bar in X client programs on Windows
- System Manager times out on agent functions such as Activate and Status Poll
- UNKNOWN program and arguments in certain alert messages
- Using HP-UX HIDS with IPFilter and SecureShell
- Unable to Generate Administrator Keys and Agent Certificates on PA–RISC 1.1 Systems
- Troubleshooting
- H HP Software License
enabled, the following alerts are issued and displayed in the GUI network nodes and logged in
the alert log file (defined by the IDS_ALERTFILE configuration variable) of the agent:
• File-related aggregated alerts
• File-related real-time alerts that could not be aggregated
• Non-file-related real-time alerts
These alerts are also sent to any response programs in the response directory, as defined by the
IDS_RESPONSEDIR configuration variable described in “Global Configuration” (page 192) (the
default is /opt/ids/response). Optionally, all real-time alerts (that is, both file and
non-file-related alerts) can also be issued concurrently by the agent when aggregation is enabled.
The real-time alerts will only be sent to response programs in the real-time response directory,
as defined by the IDS_RT_RESPONSEDIR configuration variable described in “Global
Configuration” (page 192) (the default is /opt/ids/rt_response). The ability to have a separate
set of response programs that receive real time alerts preserves the HIDS ability to do real time
automated response (that does not require human intervention such as automatically killing an
offending process) while at the same time allowing an administrator to monitor fewer alerts with
alert aggregation. When a schedule is configured to issue both aggregated alerts and real- time
alerts, the response scripts in the IDS_RT_RESPONSEDIR directory are intended primarily for
performing real-time automated response that do not require human intervention. Killing an
offending process or closing a client connection are examples of responses that can be automated.
The response scripts in the IDS_RESPONSEDIR directory in turn, are intended primarily for
reporting alerts (by email to an administrator, or to the OVO console using the HIDS OVO/SPI)
for human consumption.
Alert aggregation is enabled by default for all newly created and predefined surveillance
schedules. It can be configured either by using the GUI Schedule Manager window, or by editing
a schedule in text format. See “Surveillance Schedule Text File” (page 198) for more information
on the schedule in text format.
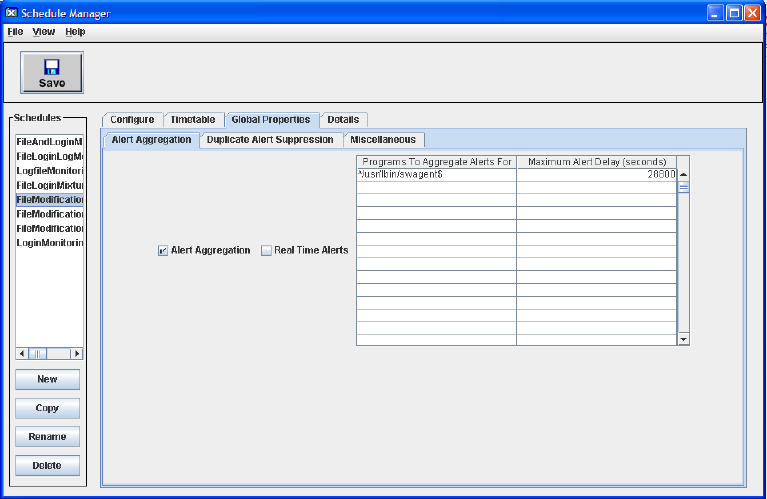
To enable and configure Alert Aggregation, follow these steps:
1. Select a schedule in the Schedules panel.
Figure 5-13 Schedule Manager Screen-Alert Aggregation Tab
2. Select the Alert Aggregation tab on the Schedule Manager screen.
3. Select the Alert Aggregation option box to enable alert aggregation.
Configuring Alert Aggregation 73