HP-UX Host Intrusion Detection System Version 4.3 administrator guide
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX Host Intrusion Detection System Version 4.3 administrator guide
- Table of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Configuring HP-UX HIDS
- 3 Getting Started with HP-UX HIDS
- 4 Using the System Manager Screen
- Starting the HP-UX HIDS System Manager
- Stopping the HP-UX HIDS System Manager
- System Manager Components
- Starting HP-UX HIDS Agents
- Getting the Status of Agent Hosts
- Resynchronizing Agent Hosts
- Activating Schedules on Agent Hosts
- Stopping Schedules on Agent Hosts
- Halting HP-UX HIDS Agents
- Accessing Other Screens
- 5 Using the Schedule Manager Screen
- The Schedule Manager
- Configuring Surveillance Schedules
- Configuring Surveillance Groups
- Configuring Detection Templates
- Setting Surveillance Schedule Timetables
- Configuring Alert Aggregation
- Configuring Monitor Failed Attempts
- Configuring Duplicate Alert Suppression
- Viewing Surveillance Schedule Details
- Predefined Surveillance Schedules and Groups
- 6 Using the Host Manager Screen
- 7 Using the Network Node Screen
- 8 Using the Preferences Screen
- A Templates and Alerts
- Alert Summary
- UNIX Regular Expressions
- Limitations
- Template Property Types
- Buffer Overflow Template
- Race Condition Template
- Modification of files/directories Template
- Changes to Log File Template
- Creation and Modification of setuid/setgid File Template
- Creation of World-Writable File Template
- Modification of Another User’s File Template
- Login/Logout Template
- Repeated Failed Logins Template
- Repeated Failed su Commands Template
- Log File Monitoring Template
- B Automated Response for Alerts
- C Tuning Schedules and Generating Alert Reports
- D The Agent Configuration File
- E The Surveillance Schedule Text File
- F Error Messages
- G Troubleshooting
- Troubleshooting
- Agent and System Manager cannot communicate with each other
- Agent complains that idds has not been enabled, yet lsdev shows /dev/idds is present
- Agent does not start on system boot
- Agent halts abnormally, leaving ids_* files and message queues
- Agent host appears to hang and/or you see message disk full
- Agent needs further troubleshooting
- Agent does not start after installation
- Agents appear to be stuck in polling status
- Agent displays error if hostname to IP mapping is not registered in name service
- Aggregated alerts targets or details field are truncated and the same aggregated alert has several entries logged in the IDS_ALERTFILE
- Alert date/time sort seems inconsistent
- Alerts are not being displayed in the alert browser
- Buffer overflow triggers false positives
- Duplicate alerts appear in System Manager
- Getting several aggregated alerts for the same process
- GUI runs out of memory after receiving around 19,000 alerts
- The idsadmin Command needs installed agent certificates
- The idsadmin Command notifies of bad certificate when pinging a remote agent
- IDS_checkInstall fails with a kmtune error
- IDS_genAdminKeys or IDS_genAgentCerts does not complete successfully
- IDS_genAdminKeys or idsgui quits early
- Large files in /var/opt/ids
- Log files are filling up
- No Agent Available
- Normal operation of an application generates heavy volume of alerts
- Reflection X rlogin produces multiple login and logout alerts
- Schedule Manager timetable screen appears to hang
- SSH does not perform a clean exit after idsagent is started
- System Manager appears to hang
- System Manager does not let you save files to specific directories
- System Manager does not start after idsgui is started
- System Manager starts with no borders or title bar in X client programs on Windows
- System Manager times out on agent functions such as Activate and Status Poll
- UNKNOWN program and arguments in certain alert messages
- Using HP-UX HIDS with IPFilter and SecureShell
- Unable to Generate Administrator Keys and Agent Certificates on PA–RISC 1.1 Systems
- Troubleshooting
- H HP Software License
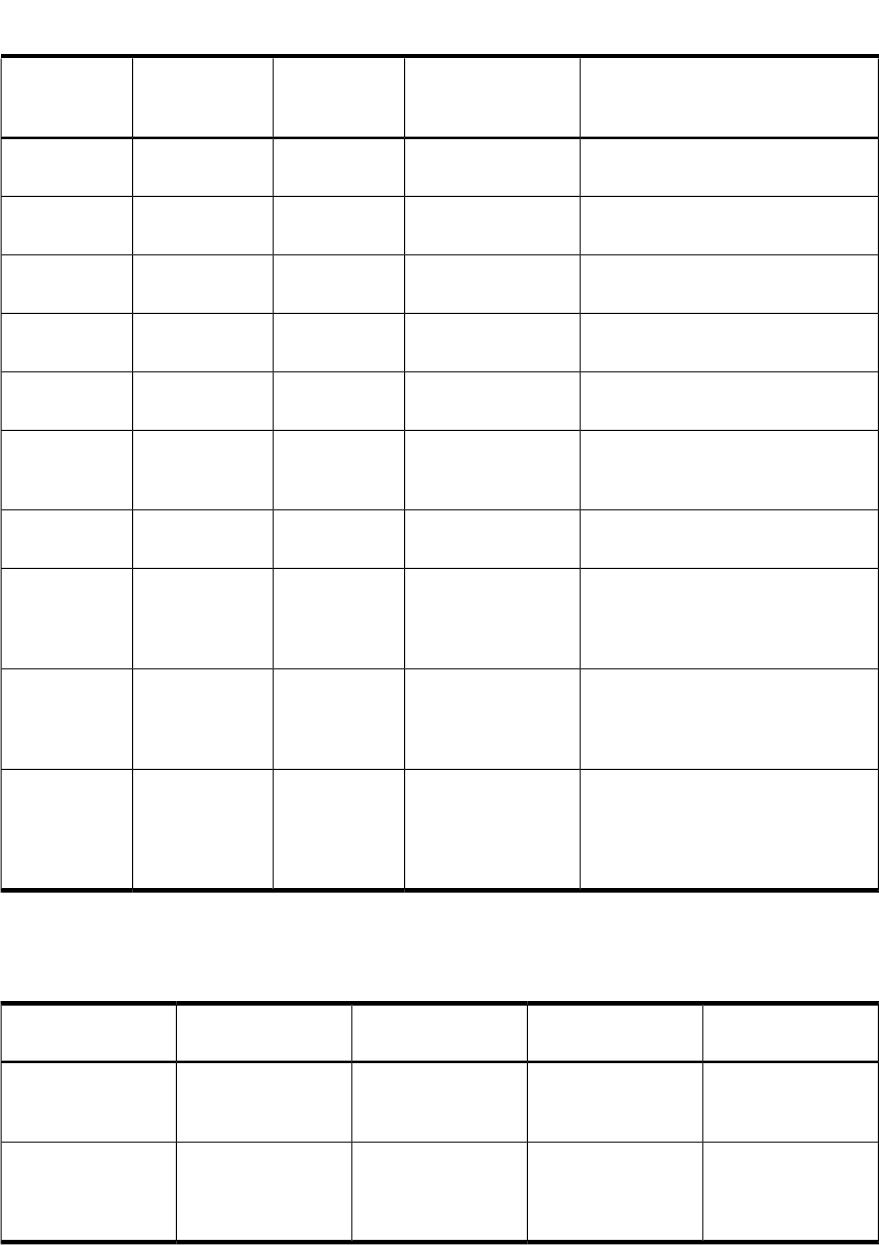
Table B-1 Additional Arguments Passed to Response Programs for Kernel Template Alerts
(continued)
DescriptionAlert Value/FormatAlert Field TypeAlert FieldResponse
Program
Argument
Mode of the attack program<mode> (decimal)IntegerAttack Program
Mode
argv[26]
Owner of the attack program (uid)<uid>IntegerAttack Program
Owner
argv[27]
Group of the attack program (gid)<gid>IntegerAttack Program
Group
argv[28]
Inode number of the attack program<inode>IntegerAttack Program
Inode
argv[29]
Device number of the attack program<device>IntegerAttack Program
Device
argv[30]
Number of arguments passed to the
attack program (for example, argc)
<argc>IntegerAttack Program
Argument
Count
argv[31]
Program arguments of the attack
program (first 1024 characters)
<argv[0]> <argv[1]>
...
StringAttack Program
Arguments
argv[32]
Name of the pty on which the
attacker is connected to (for example,
pts/ta). Set to an empty string if it is
not known.
<pty>StringAttacker
pseudo-tty
argv[33]
Full host name of remote host from
which the attacker has logged in. Set
to localhost name or to an empty
string if the local host is not known.
<hostname>StringAttacker
hostname
argv[34]
IP address (in Ipv4 or IPv6 string
notation) of the remote host from
which the attacker logged in. Set to
an empty string if the address is not
known.
<A.B.C.D> (IPv4)
or <X:X:X:....>
(IPv6)
StringAttacker IP
address
argv[35]
Table B-2 lists the additional arguments that are passed to response programs for suppressed
alerts.
Table B-2 Additional Arguments Passed to Response Programs for Suppressed Alerts
DescriptionAlert Value/ FormatAlert Field TypeAlert Field
Response Program
Argument
Number of duplicate
alerts that were
suppressed.
<number of
suppressed
alerts>
IntegerNumber of
suppressed alerts
argv[36]
Time elapsed when
duplicate alerts were
suppressed
<time unit>
IntegerUnit of time (can be
seconds, minutes,
hours, or days). The
default is seconds.
argv[37]
Table B-3 lists the additional arguments that are passed to response programs while
attempting the modification of files that belong to Modification of files/
directories template, Changes to Log File template, and Modification of
Another User’s File template.
162 Automated Response for Alerts










