HP-UX Encrypted Volume and File System Performance and Tuning
13
The read-data can only be retrieved from disk as fast as the OS, file system, and driver can process
the transactions. We will see later that tuning for read-ahead can help read throughput, but without
the buffer cache utilization that writes can benefit from, the application throughput measurement will
appear to be much less. Note that this is only the appearance – the actual write data (without the
write-behind caching benefit) moves through the OS, file system, and driver, at a rate that is similar to
reads.
The Default Sequential Reads graph shows that, for this test case, EVFS throughput is less than half of
clear I/O, and CPU utilization increases significantly. However, the rates remain constant despite the
load – as evidenced from the 10-100 IOZone Thread data points.
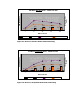
Figure 10 – Default Random Reads
Random reads show the same throughput degradation as sequential, but without noticeable CPU
utilization. Clear I/O suffers less from system load (number of threads) than the random writes test
case above, so the throughput differential is higher between clear I/O and EVFS for this test case.
64k Block Random Read - 100mb File Size
2%
7%
12%
18%
22%
4%
14%
17%
20%
20%
1 10 25 50 100
IOZone Threads
CPU Utilization %
Throughput KBs -
Scale1
Clear CPU EVFS CPU Clear Random Read EVFS Random Read