Debugging with GDB Manual (5900-1473; WDB 6.2; January 2011)
Table Of Contents
- Debugging with GDB Manual
- Contents
- Summary of GDB
- 1 A Sample GDB Session
- 1.1 Loading the Executable
- 1.2 Setting Display width
- 1.3 Setting Breakpoints
- 1.4 Running the executable under GDB
- 1.5 Stepping to the next line in the source program
- 1.6 Stepping into a subroutine
- 1.7 Examining the Stack
- 1.8 Printing Variable Values
- 1.9 Listing Source Code
- 1.10 Setting Variable Values During a Session
- 2 Getting In and Out of GDB
- 3 GDB Commands
- 4 Running Programs Under GDB
- 4.1 Compiling for debugging
- 4.2 Starting your program
- 4.3 Arguments To Your Program
- 4.4 Program Environment
- 4.5 Working directory
- 4.6 Program Input and Output
- 4.7 Debugging a Running Process
- 4.8 Killing the child process
- 4.9 Debugging programs with multiple threads
- 4.10 Debugging programs with multiple processes
- 5 Stopping and Continuing
- 6 Examining the Stack
- 7 Examining Source Files
- 8 Examining Data
- 9 Using GDB with Different Languages
- 10 Examining the Symbol Table
- 11 Altering Execution
- 12 GDB Files
- 13 Specifying a Debugging Target
- 14 HP-UX Configuration-Specific Information
- 14.1 Summary of HP Enhancements to GDB
- 14.2 HP-UX dependencies
- 14.3 Supported Platforms and Modes
- 14.4 HP-UX targets
- 14.5 Support for Alternate root
- 14.6 Specifying object file directories
- 14.7 Fix and continue debugging
- 14.8 Inline Support
- 14.9 Debugging Macros
- 14.10 Debugging Memory Problems
- 14.10.1 When to suspect a memory leak
- 14.10.2 Memory debugging restrictions
- 14.10.3 Memory Debugging Methodologies
- 14.10.4 Debugging Memory in Interactive Mode
- 14.10.5 Debugging Memory in Batch Mode
- 14.10.6 Debugging Memory Interactively After Attaching to a Running Process
- 14.10.7 Open-files reporting
- 14.10.8 Configuring memory debugging settings
- 14.10.9 Scenarios in memory debugging
- 14.10.9.1 Stop when freeing unallocated or deallocated blocks
- 14.10.9.2 Stop when freeing a block if bad writes occurred outside block boundary
- 14.10.9.3 Stop when a specified block address is allocated or deallocated
- 14.10.9.4 Scramble previous memory contents at malloc/free calls
- 14.10.9.5 Detect dangling pointers and dangling blocks
- 14.10.9.6 Detect in-block corruption of freed blocks
- 14.10.9.7 Specify the amount of guard bytes for every block of allocated memory
- 14.10.10 Comparison of Memory Debugging Commands in Interactive Mode and Batch Mode
- 14.10.11 Heap Profiling
- 14.10.12 Memory Checking Analysis for User Defined Memory Management Routines
- 14.10.13 Commands to track the change in data segment value
- 14.10.14 Support for Memory Debugging Feature on Applications Using libmallocng Library for Heap Allocation Management
- 14.11 Thread Debugging Support
- 14.11.1 Support for Enabling and Disabling Specific Threads
- 14.11.2 Backtrace Support for Thread Debugging
- 14.11.3 Advanced Thread Debugging Support
- 14.11.4 Debugging Threads Interactively After Attaching to a Process
- 14.11.5 Thread Debugging in Batch Mode
- 14.11.6 Thread Debugging in +check Mode
- 14.11.7 Known issues with Thread Debugging for Interactive and Batch mode
- 14.12 Debugging MPI Programs
- 14.13 Debugging multiple processes (programs with fork and vfork calls)
- 14.14 Command to Search for a Pattern in the Memory Address Space
- 14.15 Debugging Core Files
- 14.15.1 Generating core files with packcore /unpackcore/getcore
- 14.15.2 Support for the info target Command
- 14.15.3 Support for the dumpcore command
- 14.15.4 Support for display of run time type information
- 14.15.5 Support for Core File Debugging of MITR Applications
- 14.15.5.1 Configuring HP WDB for Mixed Mode Debugging
- 14.15.5.2 Command to Support Core File Debugging in Mixed More Applications
- 14.15.5.3 Change in the Behavior of Existing Commands
- 14.15.5.4 Command and Features Applicable to PA-RISC Libraries
- 14.15.5.5 Known Issues and Unsupported Features in Mixed Mode Debugging
- 14.15.6 Support for mmapfile command
- 14.16 Debugging with debug information available in the side debug file
- 14.17 Printing the Execution Path Entries for the Current Frame or Thread
- 14.18 Command to Unwind Beyond 10000 Frames
- 14.19 Invoking GDB Before a Program Aborts
- 14.20 Aborting a Command Line Call
- 14.21 Instruction Level Stepping
- 14.22 Enhanced support for watchpoints and breakpoints
- 14.23 Debugging support for shared libraries
- 14.23.1 Using shared library as main program
- 14.23.2 Setting Deferred Breakpoints in Shared Library
- 14.23.3 Using catch load
- 14.23.4 Privately mapping shared libraries
- 14.23.5 Selectively Mapping Shared Libraries As Private
- 14.23.6 Setting breakpoints in shared library
- 14.23.7 Enhancement to the info shared Command
- 14.24 Debugging support for Decimal Floating Point data type
- 14.25 Additional Support for binary floating point data type
- 14.26 Language support
- 14.27 Viewing Wide Character Strings
- 14.28 Support for output logging
- 14.29 Getting information from a non-debug executable
- 14.30 Debugging optimized code
- 14.31 Debugging with ARIES
- 14.32 Visual Interface for HP WDB
- 14.32.1 Starting and stopping Visual Interface for HP WDB
- 14.32.2 Navigating the Visual Interface for HP WDB display
- 14.32.3 Specifying foreground and background colors
- 14.32.4 Using the X-window graphical interface
- 14.32.5 Using the TUI mode
- 14.32.6 Changing the size of the source or debugger pane
- 14.32.7 Using commands to browse through source files
- 14.32.8 Loading source files
- 14.32.9 Editing source files
- 14.32.10 Editing the command line and command-line history
- 14.32.11 Saving the contents of a debugging session to a file
- 14.33 Support for ddd
- 14.34 Support for XDB commands
- 14.35 GDB Logging Commands
- 14.36 Support for command line calls in a stripped executable
- 14.37 Displaying the current block scope information
- 14.38 Linux support
- 14.39 Source level debugging
- 14.40 Support for using old DW-VIRTUALITY values
- 14.41 Additional support for examining registers
- 15 The HP-UX Terminal User Interface
- 16 XDB to HP WDB Transition Guide
- 16.1 By-function lists of XDB commands and HP WDB equivalents
- 16.2 Overall breakpoint commands
- 16.2.1 Auxiliary breakpoint commands
- 16.2.2 Breakpoint creation commands
- 16.2.3 Breakpoint status commands
- 16.2.4 All-procedures breakpoint commands
- 16.2.5 Global breakpoint commands
- 16.2.6 Assertion control commands
- 16.2.7 Record and playback commands
- 16.2.8 Macro facility commands
- 16.2.9 Signal control commands
- 16.2.10 Miscellaneous commands
- 16.3 XDB data formats and HP WDB equivalents
- 16.4 XDB location syntax and HP WDB equivalents
- 16.5 XDB special language operators and HP WDB equivalents
- 16.6 XDB special variables and HP WDB equivalents
- 16.7 XDB variable identifiers and HP WDB equivalents
- 16.8 Alphabetical lists of XDB commands and HP WDB equivalents
- 17 Controlling GDB
- 17.1 Setting the GDB Prompt
- 17.2 Setting Command Editing Options in GDB
- 17.3 Setting Command History Feature in GDB
- 17.4 Setting the GDB Screen Size
- 17.5 Supported Number Formats
- 17.6 Optional warnings and messages
- 17.7 Optional messages about internal happenings
- 17.8 Configuring the Current Application Binary Interface (ABI)
- 18 Canned Sequences of Commands
- 19 Using GDB under gnu Emacs
- 20 GDB Annotations
- 21 The GDB/MI Interface
- 21.1 GDB/MI Command Syntax
- 21.2 GDB/MI compatibility with CLI
- 21.3 GDB/MI output records
- 21.4 GDB/MI command description format
- 21.5 GDB/MI breakpoint table commands
- 21.6 GDB/MI Data manipulation
- 21.7 GDB/MI program control
- 21.8 Miscellaneous GDB commands in GDB/MI
- 21.9 GDB/MI Stack Manipulation Commands
- 21.10 GDB/MI Symbol query commands
- 21.11 GDB/MI Target Manipulation Commands
- 21.12 GDB/MI thread commands
- 21.13 GDB/MI tracepoint commands
- 21.14 GDB/MI variable objects
- 22 Reporting Bugs in GDB
- A Installing GDB
NOTE: In addition to the set of operations described here, we expect the GUI
implementation of a variable window to require, at least, the following operations:
• -gdb-show output-radix
• -stack-list-arguments
• -stack-list-locals
• -stack-select-frame
Introduction to variable objects in GDB/MI
The basic idea behind variable objects is the creation of a named object to represent a
variable, an expression, a memory location or even a CPU register. For each object
created, a set of operations is available for examining or changing its properties.
Furthermore, complex data types, such as C structures, are represented in a tree format.
For instance, the struct type variable is the root and the children will represent the
struct members. If a child is itself of a complex type, it will also have children of its own.
Appropriate language differences are handled for C, C++ and Java.
When returning the actual values of the objects, this facility allows for the individual
selection of the display format used in the result creation. It can be chosen among: binary,
decimal, hexadecimal, octal, and natural. Natural refers to a default format automatically
chosen based on the variable type (like decimal for an int, hex for pointers, and so
on.).
The following is the complete set of GDB/MI operations defined to access this functionality:
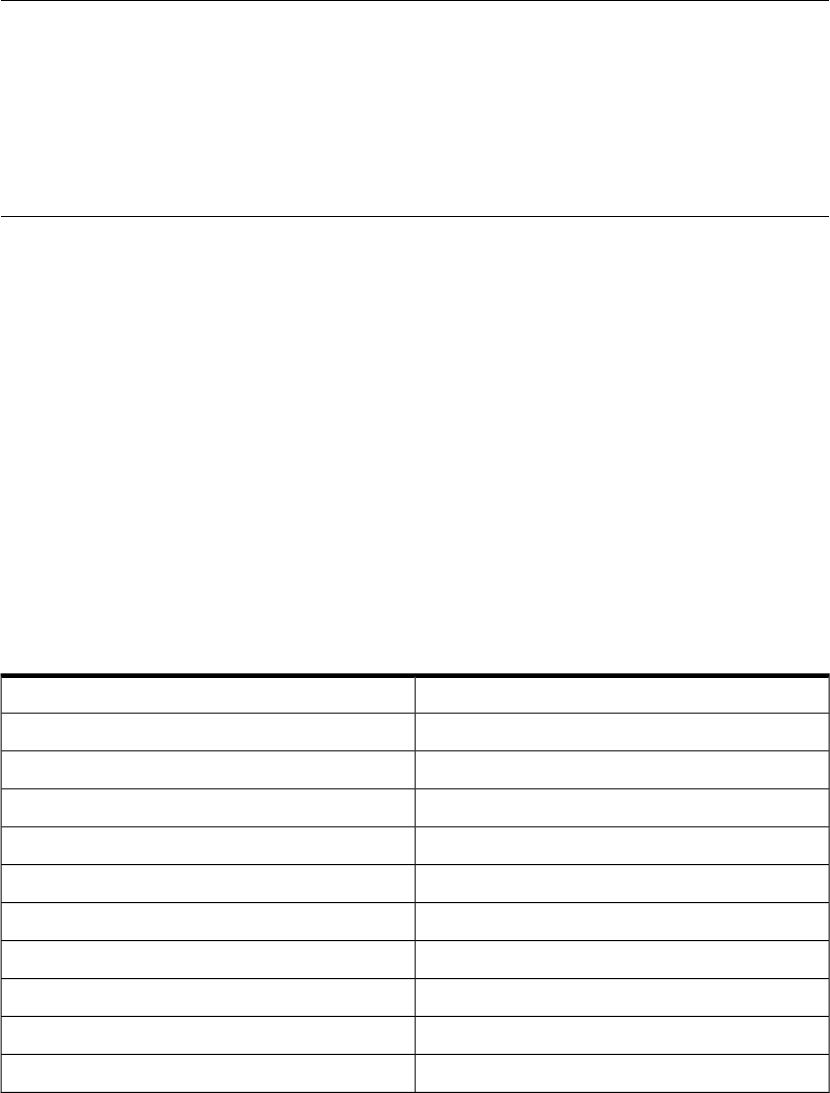
Table 33 GDB/MI Operations
DescriptionOperation
create a variable object-var-create
delete the variable object and its children-var-delete
set the display format of this variable-var-set-format
show the display format of this variable-var-show-format
tells how many children this object has-var-info-num-children
return a list of the object children-var-list-children
show the type of this variable object-var-info-type
print what this variable object represents-var-info-expression
is this variable editable? does it exist here?-var-show-attributes
get the value of this variable-var-evaluate-expression
21.14 GDB/MI variable objects 355










