HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03 (5900-2006, October 2011)
Table Of Contents
- HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03
- Contents
- About this document
- 1 Introduction to the HP CIFS Server
- 2 Installing and configuring HP CIFS Server
- HP CIFS Server requirements and limitations
- Step 1: Installing HP CIFS Server software
- Step 2: Running the configuration script
- Step 3: Modify the configuration
- Step 4: Starting HP CIFS Server
- Other Samba configuration issues
- 3 Managing HP-UX file access permissions from Windows NT/XP/2000/Vista/Windows 7
- Introduction
- UNIX file permissions and POSIX ACLs
- Using the Windows NT Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- Using the Windows Vista Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- POSIX ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- HP CIFS Server Directory ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- In conclusion
- 4 Windows style domains
- Introduction
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a PDC
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a BDC
- Domain member server
- Create the Machine Trust Accounts
- Configure domain users
- Join a Windows client to a Samba domain
- Roaming profiles
- Configuring user logon scripts
- Home drive mapping support
- Trust relationships
- 5 Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 domains
- 6 LDAP integration support
- Overview
- Network environments
- Summary of installing and configuring
- Installing and configuring your Directory Server
- Installing LDAP-UX Client Services on an HP CIFS Server
- Configuring the LDAP-UX Client Services
- Enabling Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- Extending the Samba subschema into your Directory Server
- Migrating your data to the Directory Server
- Configuring the HP CIFS Server
- Creating Samba users in directory
- Management tools
- 7 Winbind support
- 8 Kerberos support
- 9 HP CIFS deployment models
- Introduction
- Samba Domain Model
- Windows Domain Model
- Unified Domain Model
- 10 Securing HP CIFS Server
- 11 Configuring HA HP CIFS
- 12 HP-UX configuration for HP CIFS
- 13 Tool reference
- Glossary
- Index
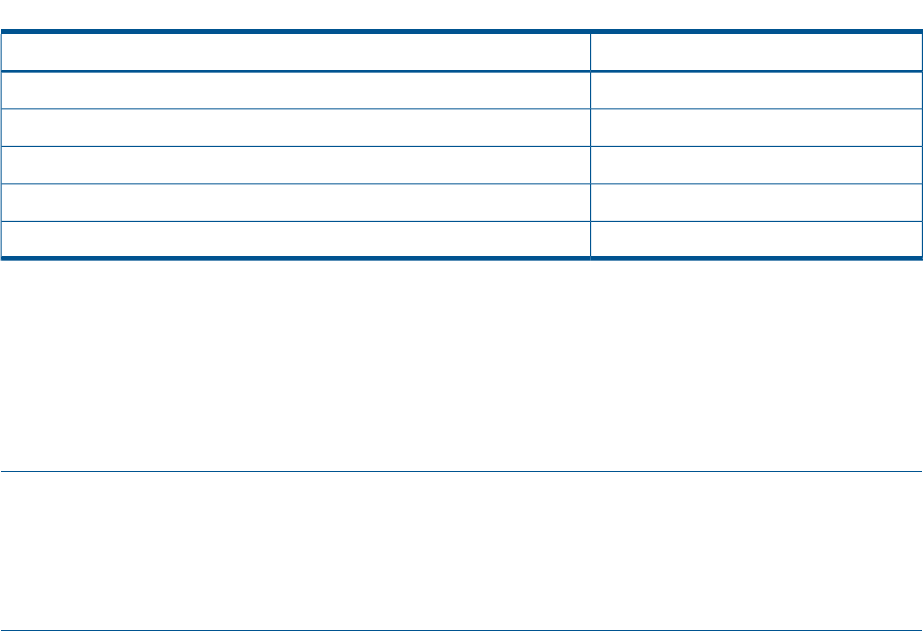
Table 9 Windows 2000 and Windows XP permissions maps UNIX permissions (continued)
UNIX permissionWindows 2000/XP
--xTraverse Folder / Execute File (Advanced)
No meaning on HP-UXDelete Subfolders and Files (Advanced)
* see explanation following tableDelete (Advanced)
* see explanation following tableChange Permissions (Advanced)
* see explanation following tableTake Ownership (Advanced)
* The Delete, Change Permissions, and Take Ownership permissions represent the file and group
ownership. You can only see these permissions, but you cannot set them from Windows 2000/XP
clients.
When the file permission is not set to Full Control, the Delete, Change and Take Ownership
permissions are shown for the file owner. Take Ownership permission is shown for the file owning
group. Everyone and other ACEs do not show these permissions except when the permission is set
to Full Control.
NOTE: The Windows 2000 permissions labeled Advanced in the table above can be viewed
from the ACL dialog box by clicking on Advanced, then View/Edit.
NOTE: The CIFS Server ensures that at least "read" permission is set for the file owner. For
example, if a user tries to set a file's permissions to "- - -", the CIFS Server will actually set it to "r
- -".
Viewing ACLs from Windows 2000 clients
1. Right-click on a file and select Properties
2. Click on the Security tab
44 Managing HP-UX file access permissions from Windows NT/XP/2000/Vista/Windows 7