HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03 (5900-2006, October 2011)
Table Of Contents
- HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03
- Contents
- About this document
- 1 Introduction to the HP CIFS Server
- 2 Installing and configuring HP CIFS Server
- HP CIFS Server requirements and limitations
- Step 1: Installing HP CIFS Server software
- Step 2: Running the configuration script
- Step 3: Modify the configuration
- Step 4: Starting HP CIFS Server
- Other Samba configuration issues
- 3 Managing HP-UX file access permissions from Windows NT/XP/2000/Vista/Windows 7
- Introduction
- UNIX file permissions and POSIX ACLs
- Using the Windows NT Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- Using the Windows Vista Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- POSIX ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- HP CIFS Server Directory ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- In conclusion
- 4 Windows style domains
- Introduction
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a PDC
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a BDC
- Domain member server
- Create the Machine Trust Accounts
- Configure domain users
- Join a Windows client to a Samba domain
- Roaming profiles
- Configuring user logon scripts
- Home drive mapping support
- Trust relationships
- 5 Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 domains
- 6 LDAP integration support
- Overview
- Network environments
- Summary of installing and configuring
- Installing and configuring your Directory Server
- Installing LDAP-UX Client Services on an HP CIFS Server
- Configuring the LDAP-UX Client Services
- Enabling Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- Extending the Samba subschema into your Directory Server
- Migrating your data to the Directory Server
- Configuring the HP CIFS Server
- Creating Samba users in directory
- Management tools
- 7 Winbind support
- 8 Kerberos support
- 9 HP CIFS deployment models
- Introduction
- Samba Domain Model
- Windows Domain Model
- Unified Domain Model
- 10 Securing HP CIFS Server
- 11 Configuring HA HP CIFS
- 12 HP-UX configuration for HP CIFS
- 13 Tool reference
- Glossary
- Index
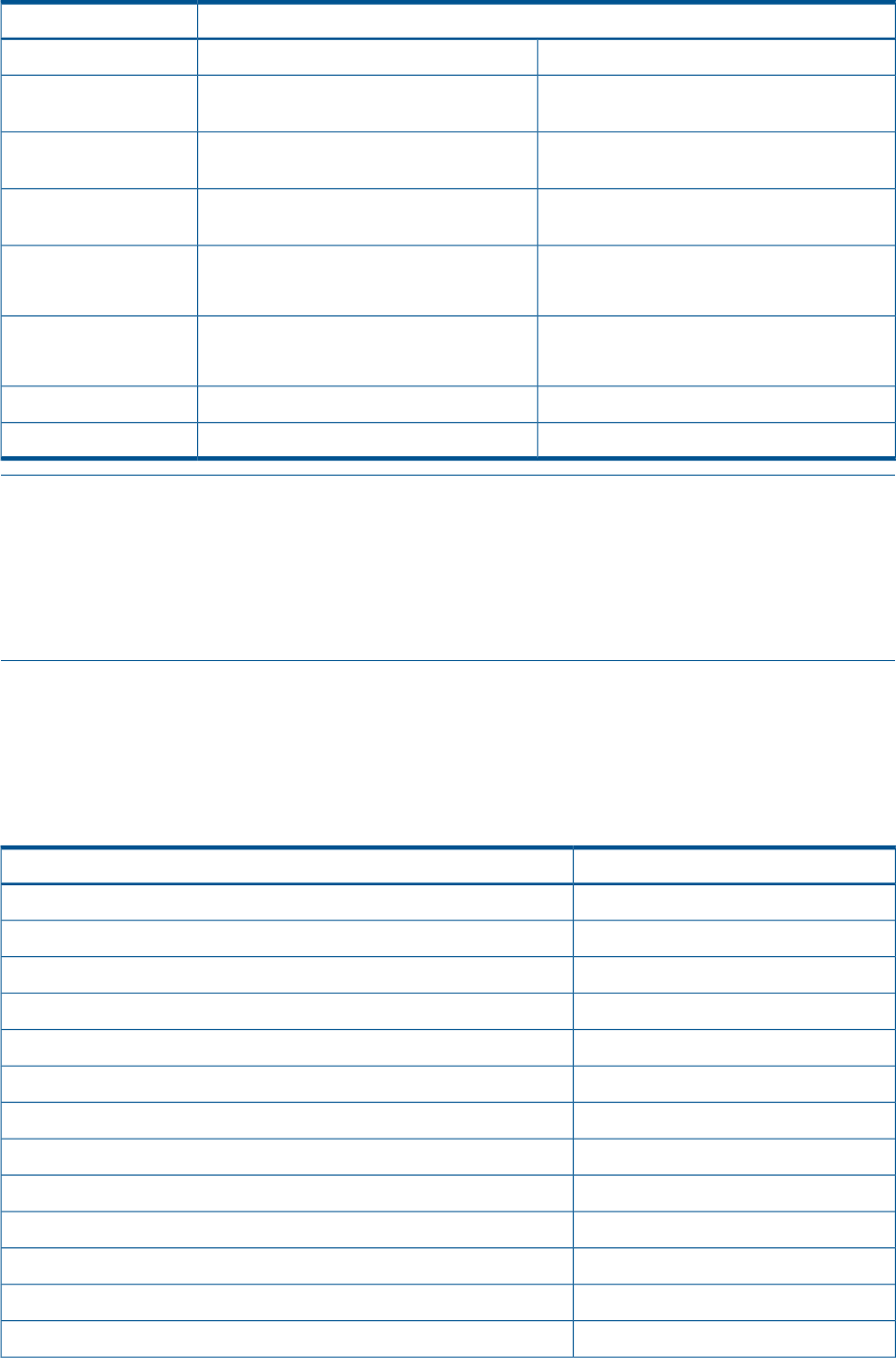
Table 8 UNIX permission maps Windows 2000/XP client permissions
Permission shown on Windows 2000/XP ClientsUNIX permission
Advanced ViewBasic View
Read Attributes, Read Extended Attributes,
Read Data, Read Permissions
Readr--
Write Attributes Write Extended Attributes,
Append Data, Write Data, Read Permissions
Write-w-
Execute or Traverse Folder, Read Attributes,
Read Permissions
None--x
All Read Permissions as in the first cellRead and Executer-x
Execute or Traverse Folder
All Read Permissions as in the first cellRead, Writerw-
All Write Permissions as in the second cell
Full Control and All permission bits are tickedFull Controlrwx
NoneNo boxes are ticked---
NOTE: In the table above, the permissions labeled Advanced can be viewed from the ACL dialog
box by clicking on Advanced, then View/Edit.
For a file owner ACE, Take Ownership, Delete and Change permissions flags are shown. For a
file's owning group ACE, Take ownership permission flag is shown.
However, all permissions are ticked in both Windows ACE Advanced and Basic views if a file
permission is Full Control.
Setting permissions from Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and
Windows 7 clients
The following table shows how each Windows 2000 and Windows XP client permission is mapped
to the UNIX permission when permissions are set from a client:
Table 9 Windows 2000 and Windows XP permissions maps UNIX permissions
UNIX permissionWindows 2000/XP
rwxFull Control
-w-Write
rwxModify
r-xRead and Execute
r--Read
r--List Folder / Read Data (Advanced)
r--Read Attributes (Advanced)
r--Read Extended Attributes (Advanced)
r--Read Permissions (Advanced)
-w-Create Files / Write Data (Advanced)
-w-Create Folder / Append Data (Advanced)
-w-Write Attributes (Advanced)
-w-Write Extended Attributes (Advanced)
POSIX ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients 43