HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03 (5900-2006, October 2011)
Table Of Contents
- HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03
- Contents
- About this document
- 1 Introduction to the HP CIFS Server
- 2 Installing and configuring HP CIFS Server
- HP CIFS Server requirements and limitations
- Step 1: Installing HP CIFS Server software
- Step 2: Running the configuration script
- Step 3: Modify the configuration
- Step 4: Starting HP CIFS Server
- Other Samba configuration issues
- 3 Managing HP-UX file access permissions from Windows NT/XP/2000/Vista/Windows 7
- Introduction
- UNIX file permissions and POSIX ACLs
- Using the Windows NT Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- Using the Windows Vista Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- POSIX ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- HP CIFS Server Directory ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- In conclusion
- 4 Windows style domains
- Introduction
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a PDC
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a BDC
- Domain member server
- Create the Machine Trust Accounts
- Configure domain users
- Join a Windows client to a Samba domain
- Roaming profiles
- Configuring user logon scripts
- Home drive mapping support
- Trust relationships
- 5 Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 domains
- 6 LDAP integration support
- Overview
- Network environments
- Summary of installing and configuring
- Installing and configuring your Directory Server
- Installing LDAP-UX Client Services on an HP CIFS Server
- Configuring the LDAP-UX Client Services
- Enabling Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- Extending the Samba subschema into your Directory Server
- Migrating your data to the Directory Server
- Configuring the HP CIFS Server
- Creating Samba users in directory
- Management tools
- 7 Winbind support
- 8 Kerberos support
- 9 HP CIFS deployment models
- Introduction
- Samba Domain Model
- Windows Domain Model
- Unified Domain Model
- 10 Securing HP CIFS Server
- 11 Configuring HA HP CIFS
- 12 HP-UX configuration for HP CIFS
- 13 Tool reference
- Glossary
- Index
group: files ldap
hosts: dns [NOTFOUND=return] files ldap
networks: files ldap
protocols: files ldap
rpc: files ldap
publickey: files
netgroup: files ldap
automount: files
aliases: files
services: files ldap
Windows Domain Model
You can use the Windows Domain Model in environments with the following characteristics:
• Deploy Windows NT4, Windows 200x Mixed Mode, or Windows 200x ADS servers (with
NetBIOS enabled).
• Support for any number of HP CIFS servers that provide file and print services for corresponding
numbers of users. It requires HP-UX LDAP Integration Client software for ADS domain member
servers.
• Access to an LDAP-UX Netscape Directory Server as the backend storage for larger deployments
to maintain winbind ID maps across multiple HP CIFS Servers.
The Windows Domain Model provides the following benefits:
• Support for Windows domain member single sign on, network logon, and Windows account
management system.
• Support for easy user management across multiple HP CIFS servers by using winbind.
• Easy expansion capability.
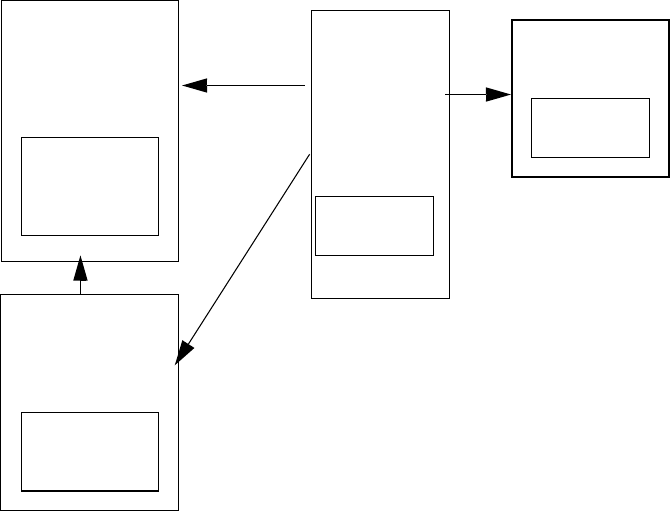
Figure 9-6 shows the Windows Domain Deployment Model as follows:
Figure 28 Windows Domain
Windows NT
Windows NT
or Windows
ADS/PDC
HP CIFS
Member
Server
LDAP
ldap-ux client
winbind daemon
libnss_winbind
idmap.tdb
idmap backend
windows
users
BDC
windows
users
idmaps
winbind
winbind
= ldap
In the Windows Domain Model, HP CIFS Server can join to a Windows domain as a member
server with Windows NT or Windows 200x domain controllers. HP CIFS Server supports winbind
to provide UID and GID mappings for Windows users. For a larger deployment environment, you
can use the LDAP directory to maintain unique ID maps across multiple HP CIFS Servers.
122 HP CIFS deployment models










