HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03 (5900-2006, October 2011)
Table Of Contents
- HP CIFS Server Administrator Guide Version A.03.01.03
- Contents
- About this document
- 1 Introduction to the HP CIFS Server
- 2 Installing and configuring HP CIFS Server
- HP CIFS Server requirements and limitations
- Step 1: Installing HP CIFS Server software
- Step 2: Running the configuration script
- Step 3: Modify the configuration
- Step 4: Starting HP CIFS Server
- Other Samba configuration issues
- 3 Managing HP-UX file access permissions from Windows NT/XP/2000/Vista/Windows 7
- Introduction
- UNIX file permissions and POSIX ACLs
- Using the Windows NT Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- Using the Windows Vista Explorer GUI to create ACLs
- POSIX ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- HP CIFS Server Directory ACLs and Windows 2000, Windows XP, Windows Vista, and Windows 7 clients
- In conclusion
- 4 Windows style domains
- Introduction
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a PDC
- Configure HP CIFS Server as a BDC
- Domain member server
- Create the Machine Trust Accounts
- Configure domain users
- Join a Windows client to a Samba domain
- Roaming profiles
- Configuring user logon scripts
- Home drive mapping support
- Trust relationships
- 5 Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 domains
- 6 LDAP integration support
- Overview
- Network environments
- Summary of installing and configuring
- Installing and configuring your Directory Server
- Installing LDAP-UX Client Services on an HP CIFS Server
- Configuring the LDAP-UX Client Services
- Enabling Secure Sockets Layer (SSL)
- Extending the Samba subschema into your Directory Server
- Migrating your data to the Directory Server
- Configuring the HP CIFS Server
- Creating Samba users in directory
- Management tools
- 7 Winbind support
- 8 Kerberos support
- 9 HP CIFS deployment models
- Introduction
- Samba Domain Model
- Windows Domain Model
- Unified Domain Model
- 10 Securing HP CIFS Server
- 11 Configuring HA HP CIFS
- 12 HP-UX configuration for HP CIFS
- 13 Tool reference
- Glossary
- Index
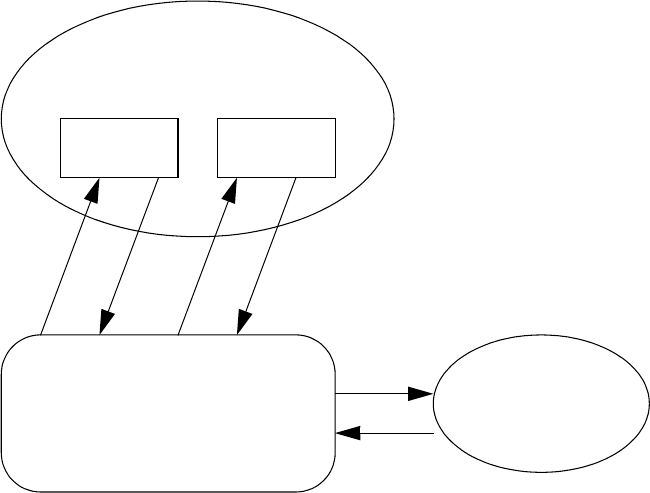
Kerberos CIFS authentication example
Figure 22 Kerberos authentication environment
indows 2000/2003 KDC
AS TGS
HP CIFS Server
Resource
1
234
6
5
W
Authenticatee
Authenticator
Windows 2000 or XP Client
The following describes a typical Kerberos logon and share service exchange using Kerberos
authentication in an Windows 2000/2003 domain environment shown in Figure 8-1:
1. The Windows Client sends the principal name and password to the Authentication Server (AS)
when running a user netlogon command.
2. The AS validates the principal and sends credentials to the Windows client, including a Ticket
Granting Ticket (TGT) and associated session key that allows the client to access the Windows
KDC.
3. The Windows client uses the session key and the TGT to request a service ticket for a share
service from Ticket Granting Service (TGS).
4. TGS sends the service ticket and other information to the Windows client.
5. The Windows client sends the service ticket to the HP CIFS Server for a share service.
6. The HP CIFS Server verifies the received information and authorizes the Windows client to
access the server's share.
HP-UX Kerberos application co-existence
The HP CIFS Server is capable of updating Kerberos keytab file. The HP CIFS Server can co-exist
with other Kerberos applications such as HP-UX Internet as described in the “Configuring
krb5.keytab” (page 112) section.
Components for Kerberos configuration
The following is a list of the various components that are necessary to configure HP CIFS Server
for Kerberos authentication:
• HP CIFS Server: Version A.02.04.02 or later (Based upon Samba 3.0.30 or later)
• HP-UX 11i v2 or HP-UX 11i v3
• HP-UX Kerberos Client
Kerberos v5 Client D.1.6.2 or later for HP-UX 11i v2◦
◦ Kerberos v5 Client E.1.6.2 or later for HP-UX 11i v3
HP-UX Kerberos application co-existence 111










