Veritas Volume Manager 5.0.1 Administrator's Guide, HP-UX 11i v3, First Edition, November 2009
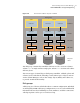
Figure 1-2
How VxVM presents the disks in a disk array as volumes to the
operating system
Veritas Volume Manager
Physical disks
Operating system
Volumes
Disk 1 Disk 2 Disk 3 Disk 4
Data can be spread across several disks within an array to distribute or balance
I/O operations across the disks. Using parallel I/O across multiple disks in this
way improves I/O performance by increasing data transfer speed and overall
throughput for the array.
Multiple paths to disk arrays
Some disk arrays provide multiple ports to access their disk devices. These ports,
coupled with the host bus adaptor (HBA) controller and any data bus or I/O
processor local to the array, make up multiple hardware paths to access the disk
devices. Such disk arrays are called multipathed disk arrays. This type of disk
array can be connected to host systems in many different configurations, (such
as multiple ports connected to different controllers on a single host, chaining of
the ports through a single controller on a host, or ports connected to different
hosts simultaneously).
See “How DMP works” on page 137.
HP-UX 11i v3 provides its own native multipathing solution in addition to the
Dynamic Multipathing (DMP) feature that is used by VxVM. These two
multipathing solutions can coexist on the same system.
See “DMP coexistence with HP-UX native multipathing” on page 143.
25Understanding Veritas Volume Manager
How VxVM handles storage management