Veritas Volume Manager 5.0 Administrator's Guide (September 2006)
33Understanding Veritas Volume Manager
Volume layouts in VxVM
Layout methods
Data in virtual objects is organized to create volumes by using the following layout
methods:
■ Concatenation and spanning
■ Striping (RAID-0)
■ Mirroring (RAID-1)
■ Striping plus mirroring (mirrored-stripe or RAID-0+1)
■ Mirroring plus striping (striped-mirror, RAID-1+0 or RAID-10)
■ RAID-5 (striping with parity)
The following sections describe each layout method.
Concatenation and spanning
Concatenation maps data in a linear manner onto one or more subdisks in a plex. To
access all of the data in a concatenated plex sequentially, data is first accessed in the first
subdisk from beginning to end. Data is then accessed in the remaining subdisks
sequentially from beginning to end, until the end of the last subdisk.
The subdisks in a concatenated plex do not have to be physically contiguous and can
belong to more than one VM disk. Concatenation using subdisks that reside on more than
one VM disk is called spanning.
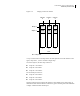
Figure 1-12 shows the concatenation of two subdisks from the same VM disk. The blocks
n, n+1, n+2 and n+3 (numbered relative to the start of the plex) are contiguous on the
plex, but actually come from two distinct subdisks on the same physical disk.
The remaining free space in the subdisk, disk01-02, on VM disk, disk01, can be put
to other uses.