Veritas Volume Manager 5.0 Administrator's Guide (September 2006)
183Creating and administering disk groups
Handling conflicting configuration copies
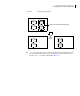
Figure 4-3 Example of a true serial split brain condition that cannot be resolved
automatically
This is a true serial split brain condition, which VxVM cannot correct automatically.
In this case, the disk group import fails, and the vxdg utility outputs error messages
similar to the following before exiting:
VxVM vxconfigd NOTICE V-5-0-33 Split Brain. da id is 0.1, while
dm id is 0.0 for DM mydg01
VxVM vxdg ERROR V-5-1-587 Disk group newdg: import failed:
Serial Split Brain detected. Run vxsplitlines
The import does not succeed even if you specify the -f flag to vxdg.
Although it is usually possible to resolve this conflict by choosing the version of the
configuration database with the highest valued configuration ID (shown as
config_tid in the output from the
vxdg list diskgroup command), this may not
be the correct thing to do in all circumstances.
The following section, “Correcting conflicting configuration information,” describes
how to fix this condition.
For more information on how to set up and maintain a remote mirror configuration,
see “Administering sites and remote mirrors” on page 423.
Disk A
Actual A = 1
Expected A = 1
Expected B = 0
Configuration
database
Disk B
Actual B = 1
Expected A = 0
Expected B = 1
Configuration
database
Shared disk group fails to import
Disk A
Actual A = 1
Expected A = 1
Expected B = 0
Configuration
database
Disk B
Actual B = 1
Expected A = 0
Expected B = 1
Configuration
database
Partial disk group
imported on host X
Partial disk group
imported on host Y
1.Disks A and B are imported
independently on separate hosts. Th
e
actual and expected serial IDs are
updated independently on each disk.
2.The disk group cannot be
reimported on the cluster. This is
because the databases do not agree o
n
the actual and expected serial IDs.
You must choose which configuratio
n
database to use.