VERITAS Volume Manager 3.1 Reference Guide
Table Of Contents
Chapter 3 113
Disk Arrays
Disk Array Overview
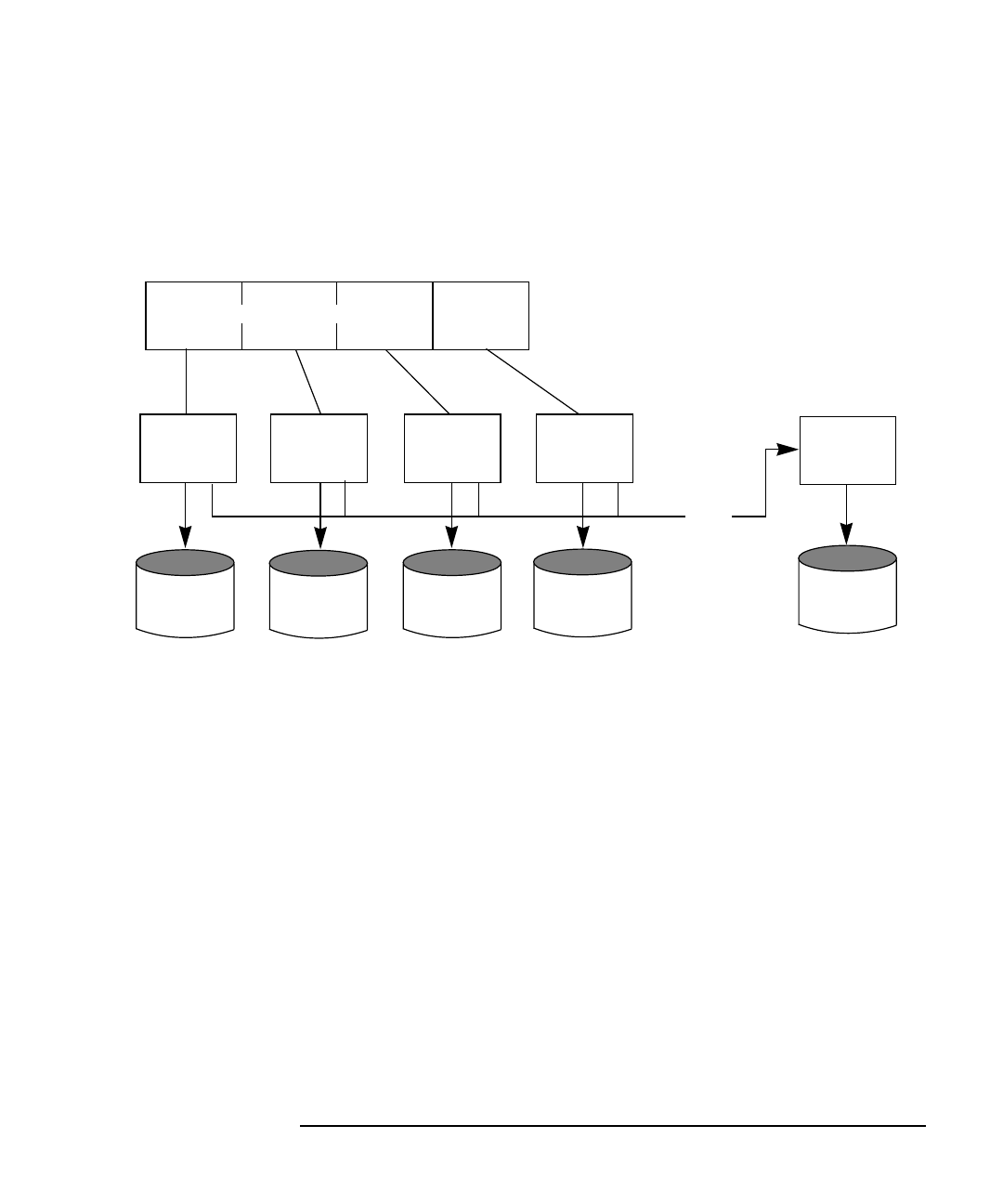
Figure 3-3, “Data Writes to RAID-3,” shows a data write to a RAID-3
array.
Figure 3-3 Data Writes to RAID-3
The parity disk model uses less disk space than mirroring, which uses
equal amounts of storage capacity for the original data and the copy.
The RAID-3 model is often used with synchronized spindles in the disk
devices. This synchronizes the disk rotation, providing constant
rotational delay. This is useful in large parallel writes.
RAID-3 type performance can be emulated by configuring RAID-5
(described later) with very small stripe units.
RAID-4
RAID-4 introduces the use of independent-access arrays (also used by
RAID-5). With this model, the system does not typically access all disks
in the array when executing a single I/O procedure. This is achieved by
ensuring that the stripe unit size is sufficiently large that the majority of
I/Os to the array will only affect a single disk (for reads).
Disk 2
Disk 1
Disk 3
Disk 4
Parity
Disk
Data for
Disk 1
Data for
Disk 2
Data for
Disk 3
Data for
Disk 4
Parity
Application Data
XOR
Data Disks










