WU-FTPD 2.6.1 release notes (5900-1547, January 2011)
Table Of Contents
- WU-FTPD 2.6.1 release notes
- Contents
- 1 WU-FTPD 2.6.1 Release Notes
- Announcement
- What Is In This Version
- WU-FTPD 2.6.1 Features
- Support for TLS/SSL
- Cryptography Algorithm
- Prerequisites for Configuring the TLS/SSL Feature
- Certificates and Authorities
- Generating Certificates and Keys Using OpenSSL 0.9.7m
- Configuring a WU-FTPD TLS Server and an FTP Client
- Configuring an FTP Server in a TLS/SSL Environment
- Configuring an FTP Client in a TLS/SSL Environment
- Basic Configuration for Secured File Transfer
- Virtual FTP Support
- Setting up Virtual FTP Support
- Support for Virtual FTP
- Without ftpservers (4) File
- Usage
- The virtual address allow usernameand virtual address deny username directives
- The virtual address private directive
- The virtual address root path and virtual address banner path directives
- The virtual address logfile path directive
- The virtual address hostname string directive
- The virtual address root path and virtual address email string directives
- The virtual address incmail emailaddress directive
- The virtual address mailfrom emailaddress directive
- Usage
- With ftpservers(4) File
- Usage
- The virtual address allow username and virtual address deny username directives
- The virtual address private directive
- The root path directive
- The banner path directive
- The logfile path directive
- The hostname some.host.name directive
- The email emailaddress directive
- The incmail emailaddress directive
- The mailfrom emailaddress directive
- Usage
- Without ftpservers (4) File
- Setting up a Virtual FTP Server
- The privatepw Utility
- New Clauses in the /etc/ftpd/ftpaccess File
- Enabling the Identification Protocol (RFC 1413)
- New Feature Related to Data Transfer
- Field Added to the /var/adm/syslog/xferlog File
- Command-Line Options
- IPv6 Support
- HP-Specific Features
- Other Features
- Support for TLS/SSL
- Changed and Removed Features
- Compatibility and Installation Information
- Known Problems and Limitations
- Related Information
- Defects Fixed in This Release
NOTE: For all these clauses, you must copy the libraries
/usr/lib/libnss_files.1 and /usr/lib/libdld.2 to the /usr/lib
directory of the current environment.
• Virtual Server
You can use the virtual server clauses to restrict user access to both the virtual and
non-virtual domains. Additionally, you can use the options specified in the virtual
clause to display the virtual host name.
The syntax for the virtual clause is as follows:
virtual <address> allow <username> [ username ...]
virtual <address> deny <username> [ username ...]
virtual <address> private
virtual <address> hostname email string
defaultserver deny <username> [ username ...]
defaultserver allow <username> [ username ...]
defaultserver private
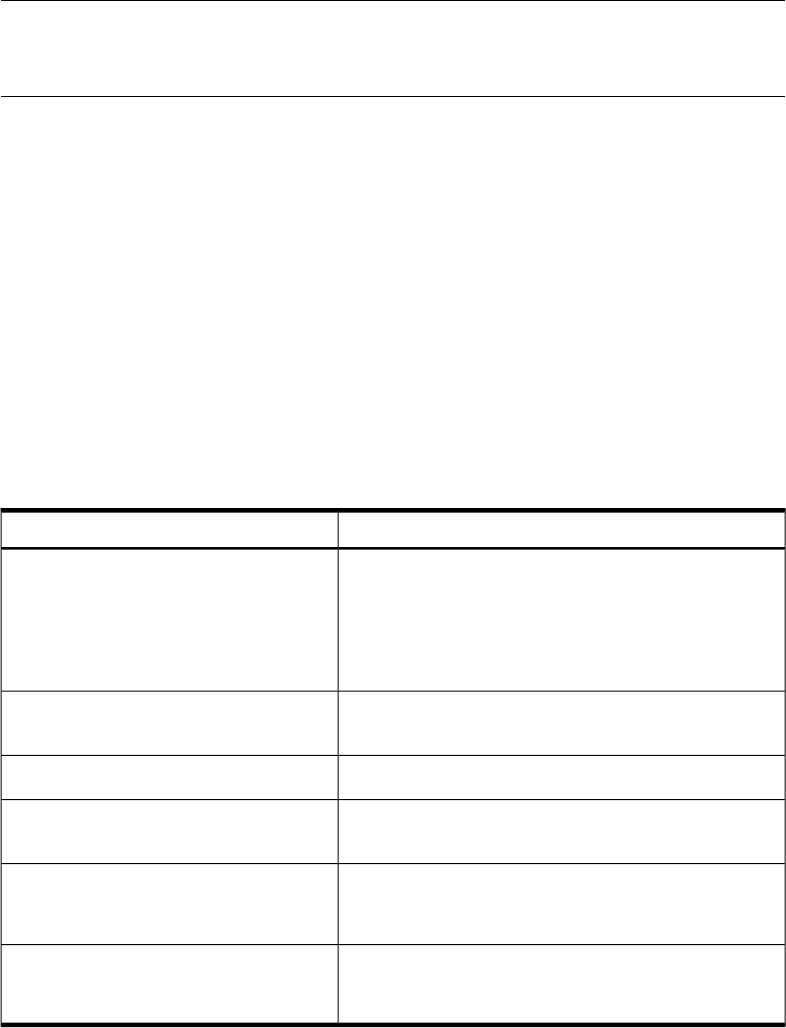
Table 2 specifies different virtual clause examples.
Table 2 The virtual Clause Options
DescriptionThe virtual Clause Option
Allows the root user to start an FTP session on the system
xx.xx.xx.xx. By default, real and guest users are not
allowed to log in to the virtual server unless they are
guests and have changed their directory to the virtual
root directory. This is applicable only for virtual FTP
servers.
virtual xx.xx.xx.xx allow root
Denies root users and allows other users to start the FTP
session.
virtual xx.xx.xx.xx allow *
virtual xx.xx.xx.xx deny root
Denies service to anonymous FTP users.
virtual xx.xx.xx.xx private
Prints the string (telnet2.abc) instead of the actual
host name in the greeting message and STAT command.
virtual xx.xx.xx.xx hostname
telnet2.abc
Denies ftp on the default FTP server for the root user.
The message FTP LOGIN REFUSEDis logged in the
/var/adm/syslog file.
defaultserver deny root
Denies anonymous ftp connection to the default server.
The message FTP LOGIN REFUSED is logged in the
/var/adm/syslog file.
defaultserver private
32 WU-FTPD 2.6.1 Release Notes










