HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
DRAFT COPY Network Addressing
Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
Chapter 7 123
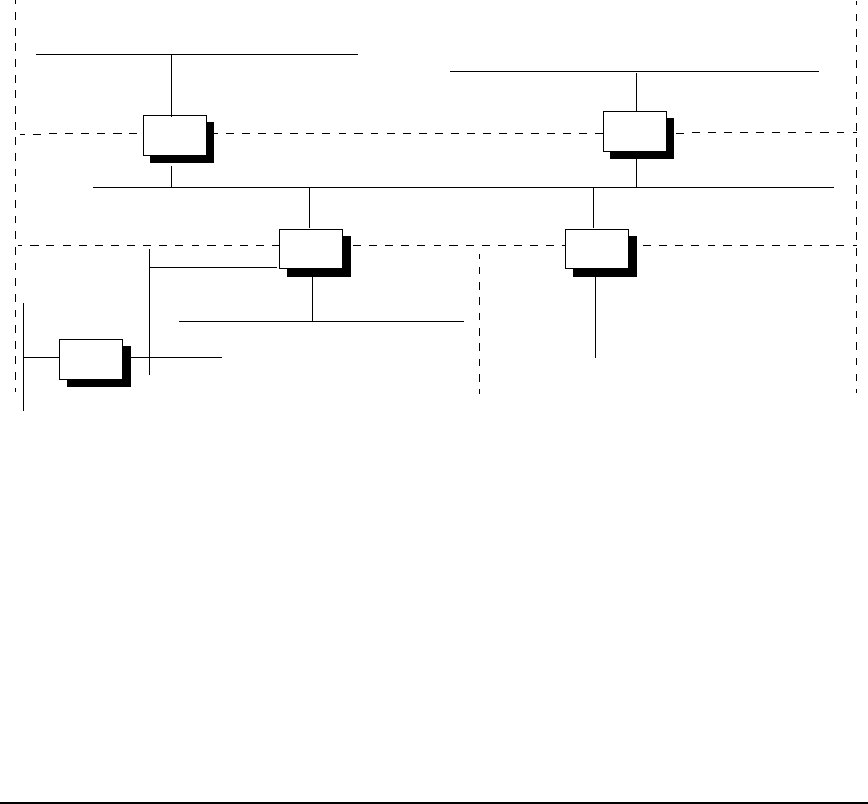
Example of Subnets with Variable-Length Subnet Masks
The following example shows four subnetworks within the 192.6.12 network along with the
netconf entries necessary to configure these subnetworks with variable-length subnet masks.
Note that there are four different subnet masks used in this network. Also note that the
subnet numbers in the network map correspond to the mirror image subnet numbers listed in
Table 7-7.
Figure 7-13 Network Map with Variable-Length Subnets
The subnet numbers shown below correspond to the subnets show in the network map in
Figure 7-13.
In this example of mirror image counting, the first subnet has 6 hosts (with space allocated for
a maximum of 6 hosts), the second subnet has 60 hosts (with space allocated for a maximum
of 62 hosts), the third subnet has 30 hosts (with space allocated for a maximum of 30 hosts),
and the fourth subnet has 14 hosts (with space allocated for a maximum of 16 hosts). Notice
how the range of numbers (129-135, 65-127,193-223, and 33-47) is spread out to allow room
for additional growth in each case.
A
C
192.6.12.64,
255.255.255.192
B
192.6.12.192,
255.255.255.224
D
Corporate Offices
Marketing Dept.
(Subnet 1) R & D Dept.
(Subnet 6)
Facility LAN
(Subnet 16)
Manufacturing Dept.
(Subnet 2)
lan1
192.6.12.64,
255.255.255.192
lan0
192.6.12.129,
255.255.255.248
lan1
192.6.12.193,
255.255.255.224
lan0
192.6.12.130,
255.255.255.248
192.6.12.132
255.255.255.248
(Gateway)
lan1
192.6.20.1
(network 192.6.20)
lan0
192.6.12.131,
255.255.255.248
lan1
192.6.12.33,
255.255.255.240
192.6.12.128,
255.255.255.248
192.6.12.32,
255.255.255.240
E
Networking LAN
(Subnet 17)
lan2
192.6.12.1
192.6.12.2.
lan1
255.255.255.128










