HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
DRAFT COPY Network Addressing
Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
Chapter 7 121
Variable-length subnet masks are assigned using the netmask parameter of the ifconfig
command, SUBNET_MASK in netconf with a 32-bit subnet mask indicated in dot notation,
or SAM. In the example below with a Class C IP address, the host portion has three types of
assigned bits: subnet number bits, growth bits, and host bits, with a chosen subnet mask that
allows for growth in both the host field and subnet field without a mask change.
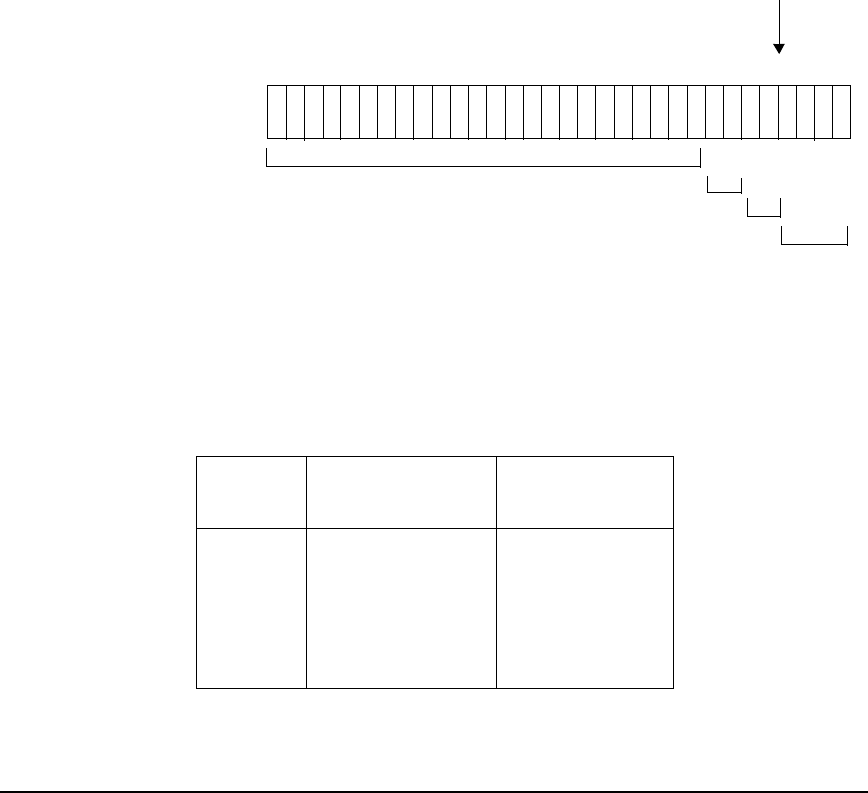
Figure 7-12 Example of Variable-Length Subnet Mask
The example below shows how the bits might look in the host address portion of a Class C
address in a network with four subnets using variable-length subnetting. In this example “g”
stands for growth bits and “h” stands for host bits. The 0’s and 1’s in the host address are
assigned subnet numbers.
Table 7-8 Subnets with Variable-Length Subnet Mask
Subnet
Host Address
(Bits)
Subnet Mask
(Bits)
A 10gg gghh 1111 1100
B 01gg ghhh 1111 1000
C 110g ghhh 1111 1000
D 001g ghhh 1111 1000
11 1111111111 11111111111011111 000
subnet portion of host address
growth portion of host address
host portion of host address
Predetermined
boundary
Class C Subnet Mask:
network address
255 . 255 . 255 . 240










