HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
DRAFT COPY Network Addressing
Subnet Addresses
Chapter 7 109
Fixed-Length Subnet Addressing
This section shows you how to apply a fixed-length subnet addressing scheme on a class C
network. The same steps may be applied on a Class A or Class B network.
Assigning a Fixed-Length Subnet Mask
Subnet addressing is implemented by specifying a 32-bit subnet mask in the ifconfig
command or the netconf file when a LAN interface card is assigned an internet address. All
nodes on a subnet must have the same subnet mask. Under the fixed-length subnet address
scheme, all subnets on a network, must have the same subnet mask.
The subnet mask is ANDed with the address attached to a message coming across the
network to determine if that message should be routed to a node on the local network or
ignored.
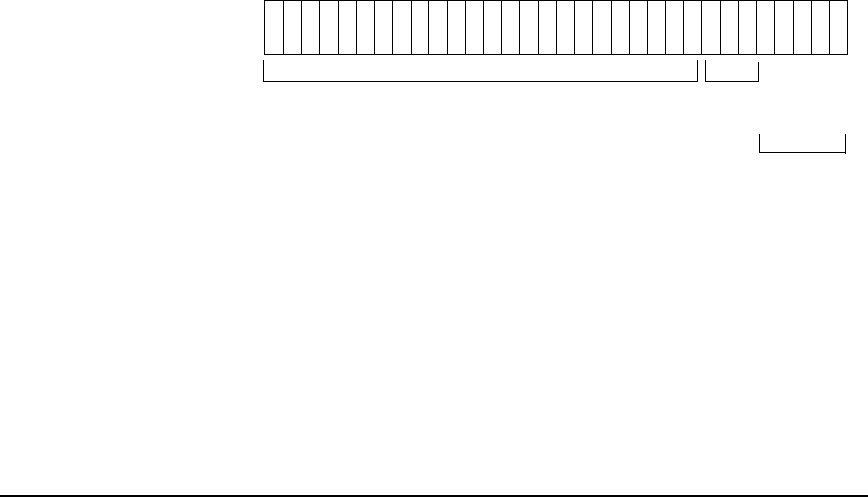
Before a subnet mask is applied, the first three octets of a Class C IP address represent the
network address. If the subnet mask 255.255.255.224 is applied, the first three octets of the
address and the first three bits of the last octet indicate the subnet address while the last five
bits of the last octet indicate the host address. This is shown in the following figure.
Figure 7-6 Fixed-Length Subnet Mask Example
With this subnet mask, up to 8 subnets with 30 nodes per subnet are possible. Table 7-5 below
lists the valid internet address ranges for nodes in a network with the subnet mask
255.255.255.224.
11 111111111111111111110011111 000
Class C Subnet Mask:
255 . 255 . 255 . 224
network address subnet portion of
host address
host portion of
host address