HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
Network AddressingDRAFT COPY
Subnet Addresses
Chapter 7108
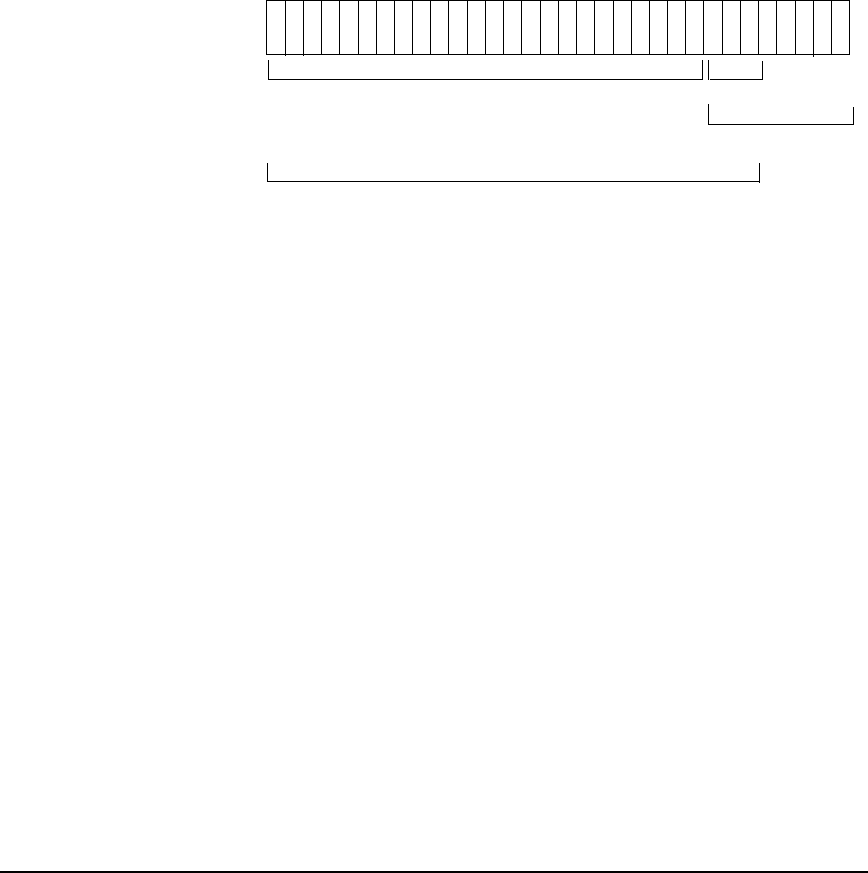
Refer to Figure 7-5 earlier in this chapter for an illustration of how the subnet mask is ANDed
with the IP address to form the subnet number.
Figure 7-5 Subnet Address and Subnet Number of Class C Internet Address
192.6.12.33
The following rules apply when choosing a subnet addressing scheme and an internet
address:
• All subnets on the same network must have the same network address.
• If your system is attached to more than one physical network, the subnet addresses of the
interfaces on your system cannot be the same.
• Do not assign a host address where all the bits of the host number are 0 or all the bits are
1.
You may choose a fixed-length subnet addressing scheme in which one subnet mask will be
used in all subnets in your network. You may also choose a variable-length subnet addressing
scheme in which the subnet masks may be varied depending on the size of the subnets you
want.
If you wish to implement variable-length subnetting, first read the conceptual information,
“Assigning Variable-Length Subnet Addresses” later in this chapter. Then refer to the specific
task-oriented instructions in the “Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN” chapter
earlier in this manual. For additional information, refer to the following online man pages:
ifconfig(1M), netstat(1), ppl.remotes(4), routing(7), and route(1M). Detailed
descriptions of fixed-length and variable-length subnet addressing follow.
11 000000110000011000010000000 001
192 . 6 . 12 . 33
Class C
IP Address:
network address = 192.6.12 subnet number = 1
host address = 33
subnet address = 192.6.12.32