HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
DRAFT COPY Network Addressing
Internet Addresses
Chapter 7 103
NOTE When specifying internet addresses, do not use leading zeroes within address
fields. For example: 192.006.012.023 is incorrect; 192.6.12.23 is correct.
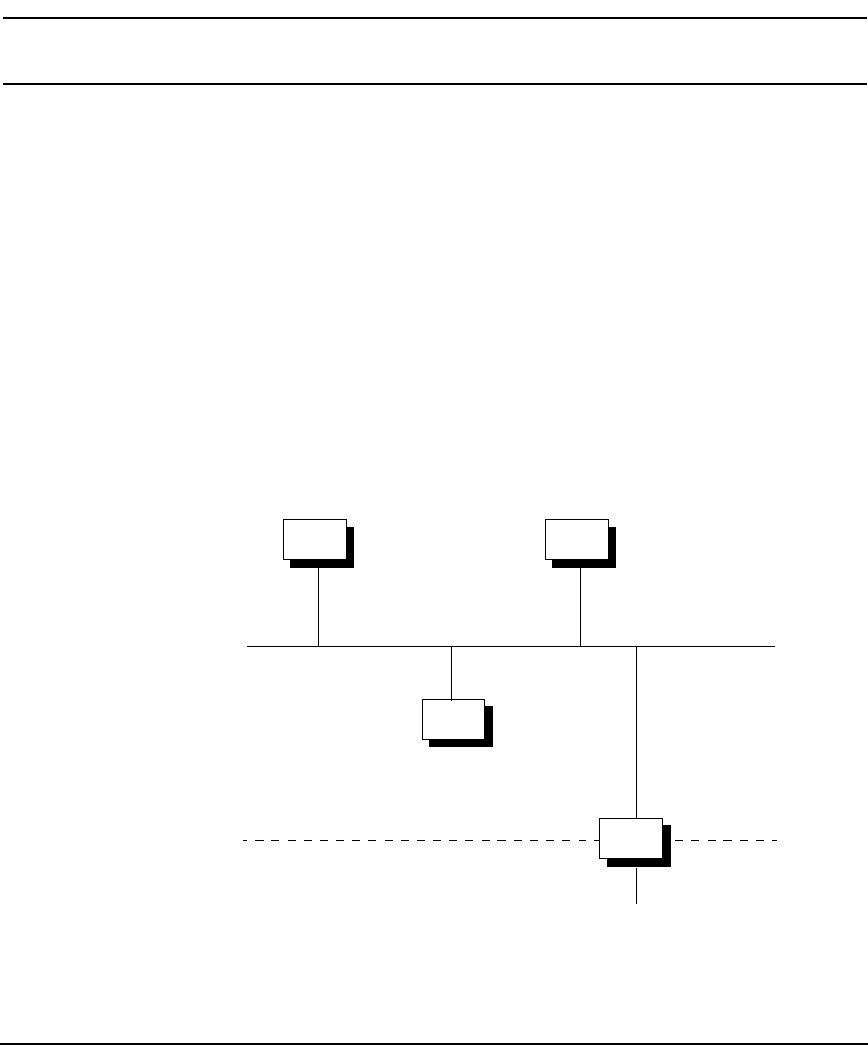
Assigning Network Addresses
To assign network addresses, follow these rules:
• You must have a network address for each logical network.
• If your system is attached to more than one physical network via a gateway, the network
addresses of these interfaces may not be the same. Refer to Table 7-3 below for a gateway
example.
• All nodes in the same network, however, must have the same network address.
• Do not assign the network addresses 0 or 255 (Class A), 0.0 or 255.255 (Class B), or 0.0.0
or 255.255.255 (Class C) to any network. Those addresses are reserved.
• Do not assign Class A network address 127. This address is reserved for the loopback
interface.
Figure 7-3 Assigning Network Addresses
A
D
B
C
Gateway
192.6.12
192.6.20










