HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
Network AddressingDRAFT COPY
Internet Addresses
Chapter 7102
where n is a number from 0 to 255, inclusive. This form is referred to as decimal dot notation
or dot notation.
Table 7-4 lists the number of networks and nodes and the address ranges for Class A, Class B,
and Class C networks. Class D networks are described later in this chapter in “IP Multicast
Addresses.”
To determine a network address and host address from an internet address, you must
separate the network and host address fields. For example, the bit representation of internet
address 192.6.1.1 is separated as follows:
Figure 7-2 Bit Representation of Internet Address
Assigning an Internet Address
Each node on the network has at least one internet address. When assigning internet
addresses, you must determine network addresses and host addresses as described in this
section.
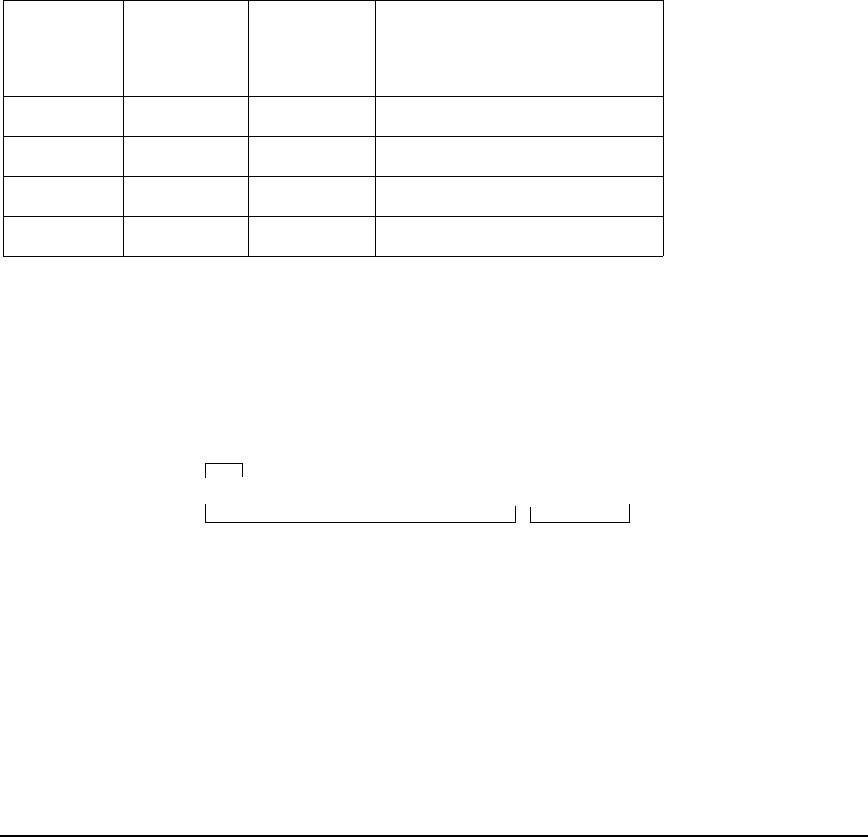
Table 7-4 Internet Address Classes
Class Networks
Nodes
per
Network
Address Range
A 127 16777215 1.0.0.1 – 126.255.255.254
B 16383 65535 128.1.0.1 – 191.255.255.254
C 2097151 255 192.0.1.1 – 223.255.255.254
Reserved - - 224.0.0.0 – 255.255.255.255
indicates
Class C
11000000.00000110.00000001.00000001
Network Address = 192.6.1 Host Address = 1










