HP-UX LAN Administrator's Guide (Feburary 2007)
Table Of Contents
- About This Document
- 1 New for the HP-UX 11i v3 Release
- 2 Installing HP-UX LAN
- 3 Configuring HP-UX LAN Using SAM
- 4 Manually Installing and Configuring HP-UX LAN
- 5 Troubleshooting HP-UX LAN
- Troubleshooting Overview
- Troubleshooting Q & A
- LAN Interface Card Statistics
- 100Base-T Checklist
- Diagnostic Flowcharts
- Flowchart 1: Configuration Test
- Flowchart 2: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 3: Configuration Test continued
- Flowchart 4: Network Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 5: Network Level Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 6: Transport Level Loopback Test (using Internet Services)
- Flowchart 7: Link Level Loopback Test
- Flowchart 8: LAN Connections Test
- Flowchart 9: Gateway Remote Loopback Test
- Flowchart 10: Gateway Remote Loopback Test continued
- Flowchart 11: Subnet Test
- 6 LAN Resources
- 7 Network Addressing
- Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
- Networking Terminology
- Network Addresses and Node Names
- Internet Addresses
- Subnet Addresses
- Configuring Gateways on Fixed-Length Subnets
- Variable-Length Subnet Addressing
- Configuring Gateways on Variable-Length Subnets
- Configuring Gateways on Supernets
- IP Multicast Addresses
- Virtual IP (VIP) Addresses
- CIDR - Classless Inter-Domain Routing
- 8 LAN Device and Interface Terminology
DRAFT COPY Network Addressing
Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
Chapter 7 91
Overview of Network Addressing Schemes
On the HP-UX 11i v3 Release, Hewlett-Packard offers several types of addressing schemes.
Table 7-1 below shows the advantages and disadvantages of each type of scheme.
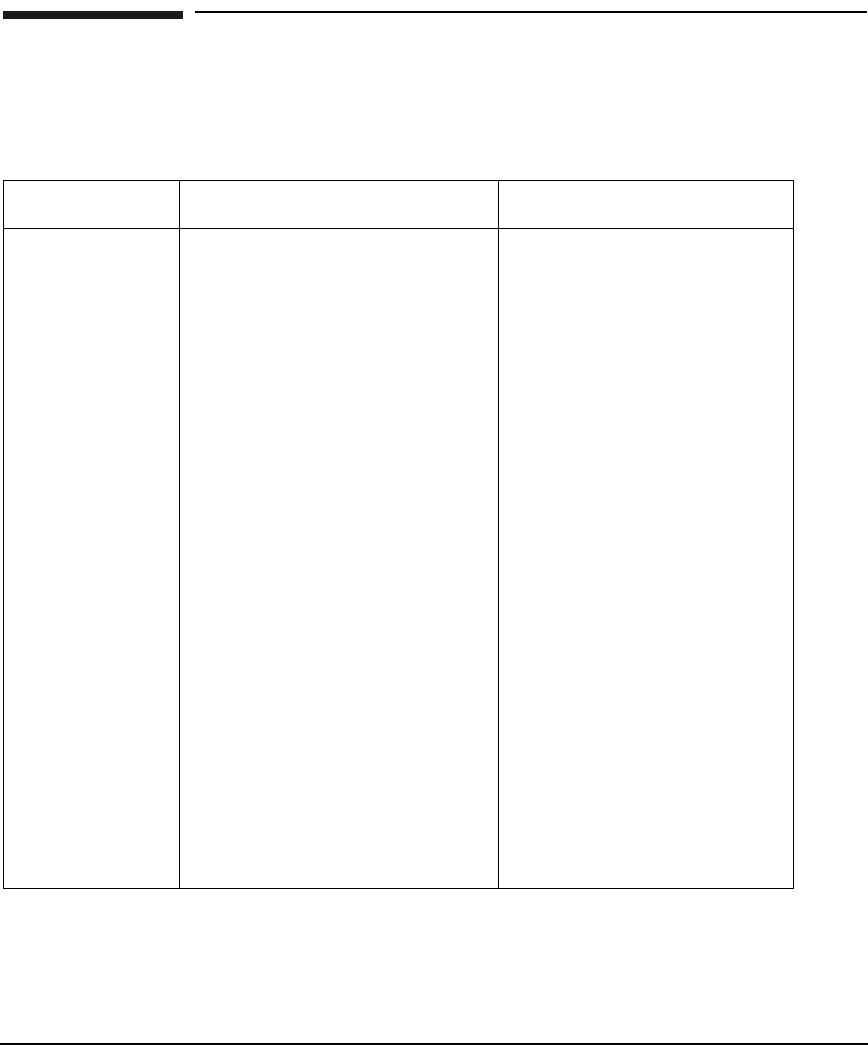
Table 7-1 Comparison of Subnet and Supernet Addressing Schemes
Address Type Advantages Disadvantages
Fixed-Length
Subnet
Addressing
Simplicity
- same netmask across network
- same size subnets across the
network
Inefficiency & Inflexibility
- waste of address space
- same size subnets across
the network
- cannot grow subnet beyond
the fixed size
Variable-Length
Subnet
Addressing
Efficiency & Flexibility
- address space allocated
according to projected size of
subnets
- variability in subnet size
- expandability in subnet size
- grow subnet by changing
subnet mask only
Complexity
- keeping track of subnet
ranges
- keeping track of netmasks
Supernet
Addressing
Simplicity
- same netmask across subnets
- no gateway configuration for
networks
Network Impact
- performance. Network
bandwidth is shared by all
nodes in the supernet.
- requires bridges if the
supernet is spread across
multiple physical networks










