Locality-Optimized Resource Alignment for Superdome 2
Table Of Contents
- Locality-Optimized Resource Alignment for Superdome 2
- Executive summary
- Background and motivation of LORA
- LORA configuration rules
- LORA system administration
- Benefits
- Summary
- Glossary
- Technical details
- Configuring nPartitions for LORA
- Configuring vPars for LORA
- Advanced tuning
- For more information
- Call to action
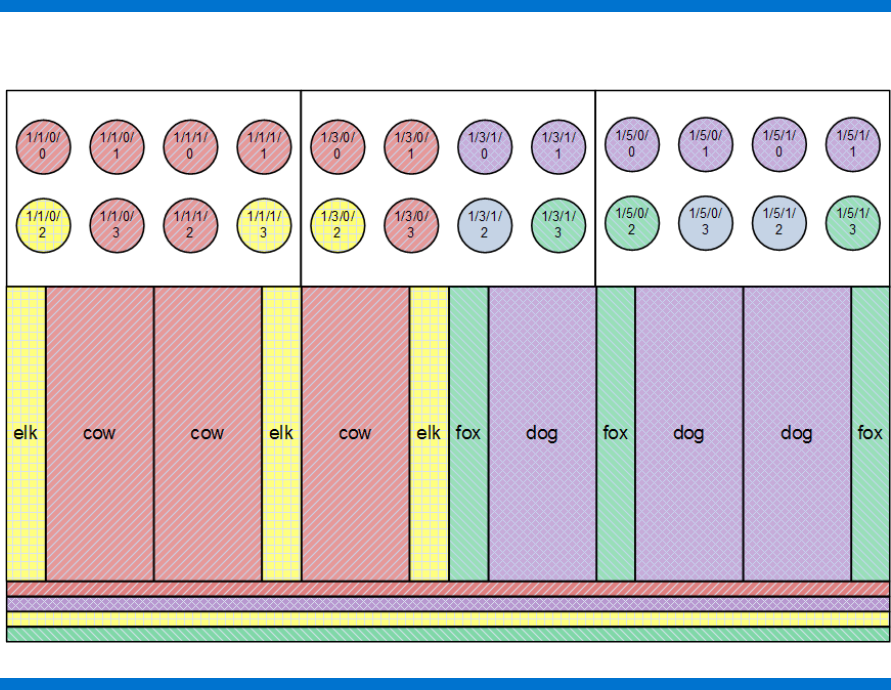
15
along with three processor cores. It is necessary to split each instance across three sockets, which is
generally undesirable; but, that cannot be avoided in this particular case. The diagram in Figure 6
shows the result:
Figure 6. The last two virtual partitions added to the LORA configuration
If we had started at the bottom of the table, and configured the instances elk and fox first, each one
could have been confined to one single socket, which would have given them superb performance.
However, it would then have been necessary to spread both cow and dog across four different
sockets, which would have given them lower performance. In general, one would assume that the
larger virtual partitions are the ones whose performance is more critical because more resources are
devoted to them. Therefore, configure the largest instances first, to give them the most compact
layout, then configure the smaller instances from the remaining resources.
Helpful hints
The rules for configuring vPars for LORA are simple:
• Draw resources for each virtual partition from the minimal number of distinct sockets
• If the number of sockets is greater than one, balance the resources across those sockets
• Do the best you can with instances created from remaining resources
If it is desired to divide an nPartition into a number of virtual partitions of equal size, it helps if that
number is a power-of-two multiple or power-of-two fraction of the number of sockets. For example, if
the nPartition is composed of 3 blades (6 sockets), then it works well to have 3, 6, or 12 virtual










