Locality-Optimized Resource Alignment for Superdome 2
Table Of Contents
- Locality-Optimized Resource Alignment for Superdome 2
- Executive summary
- Background and motivation of LORA
- LORA configuration rules
- LORA system administration
- Benefits
- Summary
- Glossary
- Technical details
- Configuring nPartitions for LORA
- Configuring vPars for LORA
- Advanced tuning
- For more information
- Call to action
11
vparcreate -N 2 -p vp1 -a socket:1/1/0:cpu::4 -a mem::4096 -a
socket:1/1/0:mem::28672
vparcreate -N 2 -p vp2 -a socket:1/1/1:cpu::4 -a mem::4096 -a
socket:1/1/1:mem::28672
vparcreate -N 2 -p vp3 -a socket:1/3/0:cpu::4 -a mem::4096 -a
socket:1/3/0:mem::28672
vparcreate -N 2 -p vp4 -a socket:1/3/1:cpu::4 -a mem::4096 -a
socket:1/3/1:mem::28672
vparcreate -N 2 -p vp5 -a socket:1/5/0:cpu::4 -a mem::4096 -a
socket:1/5/0:mem::28672
vparcreate -N 2 -p vp6 -a socket:1/5/1:cpu::4 -a mem::4096 -a
socket:1/5/1:mem::28672
The creation commands did not specify any I/O allocations. The needed I/O could be added with
subsequent commands.
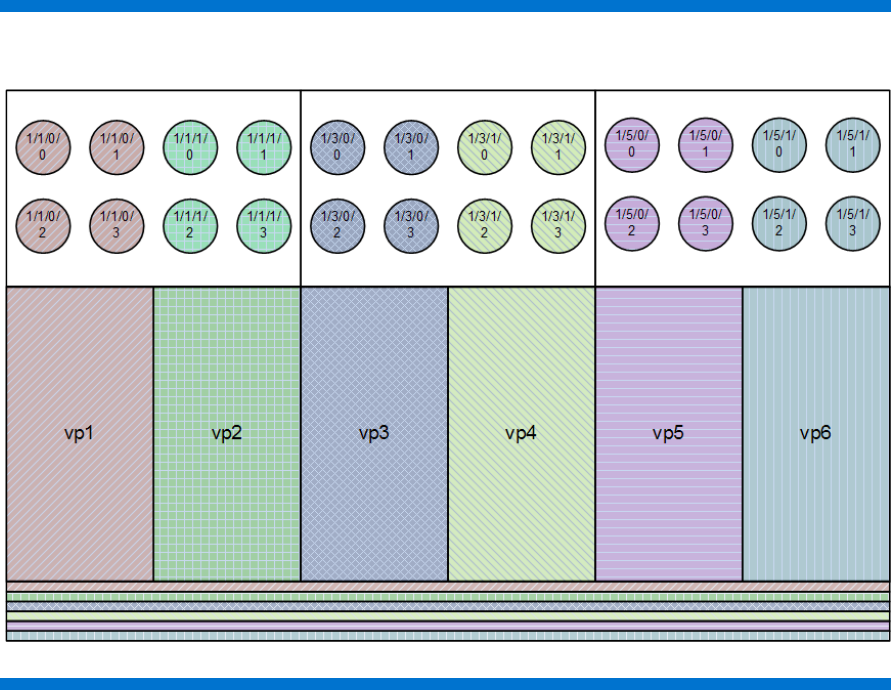
For this example, the processor and memory allocations would be as shown in the following diagram:
Figure 3. Six equal virtual partitions configured according to LORA rules
This first example was extremely simple: the resources on each blade were divided in half. But it
shows quite clearly the power behind the LORA concept: the alignment between processor cores and
local memory guarantees that the preponderance of memory references will be satisfied through the
fastest hardware path.
A slightly more complicated example involves dividing the nPartition into four equal virtual partitions.
Each instance must have 6 cores and 48 GB of memory, of which 42 GB is local memory and 6 GB










