HP-UX IP Address and Client Management Administrator's Guide (October 2009)
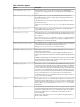
Table 1-16 Query Address Options
DescriptionOption
Specifies the address and the port used to query other name servers if a
server is unable to answer a query.
query-source [ address
(ip_addr |*)]
[port(ip_port|*)] ;
Specifies the address and the port used for queries that are sent over an
IPv6 connection.
query-source-v6 [ address
(ip_addr |*)]
[port(ip_port|*)] ;
RR Set Ordering Option
When multiple records are returned in a answer, you must configure the order of the records
placed in the response. The rrset-order option enables you to configure the order of the
records in a multiple record response.
Following is the syntax of the rrset-order option:
rrset-order { [ class class_name ] [ type type_name ] [ name
"domain_name" ] order ordering}
Following is an example of the rrset-order option:
rrset-order { class IN type A name "host.example.com" order random;
order cyclic; };
Dual-Stack Server Option
BIND provides transition support for IPv4 and IPv6 to solve problems caused by the lack of
support for either IPv4 or IPv6 address on a host system. It also provides the
dual-stack-servers option to enable the transition support for IPv4 and IPv6 addresses.
This option specifies host names or addresses of systems that have access to both IPv4 and IPv6
transports. If the host name is specified, a name server resolves a host name using the transport
supported by the name server. The dual-stack-servers option does not have any affect in
a dual-stacked system, if access to the IPv4 or IPv6 transport is disabled using the named -4 or
named -6 command.
The syntax for the dual-stack-servers option in the options statement in the /etc/
named.conf file is as follows:
[ dual-stack-servers [port ip_port] { ( domain_name [port ip_port] |
ip_addr [port ip_port] ) ; ... }; ]
Additional Options
Following are some additional options in the options statement:
• tkey-domain
This option specifies the domain name that is appended to the shared keys generated by
TKEY. When a client requests a TKEY exchange, it may or may not specify the desired name
for the key. If the client specifies the desired name for the key, the shared key name is a
combination of the client-specified part and the tkey-domain; otherwise, the shared key
name is a combination of the random hexadecimal digits and the tkey-domain. In most
cases, the domain name must be the server’s domain name.
• tkey-dhkey
This option specifies the Diffie-Hellman key used by the server to generate shared keys
with clients using the Diffie-Hellman mode of TKEY. The server must be able to load
40 Overview