Tunable Kernel Parameters
Table Of Contents
- Tunable Kernel Parameters
- Legal Notices
- Revision History
- Conventions
- 1 Overview
- 2 Accounting Subsystem
- 3 Asynchronous I/O Subsystem
- 4 File System Subsystem
- 5 Interprocess Communication (IPC) Subsystem
- 6 Kernel Crash Dump Subsystem
- 7 Memory Paging Subsystem
- 8 Process Management Subsystem
- 9 Spinlock Pool
- 10 Streams Subsystem
- 11 Miscellaneous Parameters
- Miscellaneous Parameter Summary
- CD-ROM Parameter Summary
- System Clock Parameter Summary
- Disk I/O Parameter Summary
- Intrusion Detection System/9000
- Fast Symbolic Link Traversal Parameter Summary
- Reserved System Memory Parameter Summary
- Network Parameter Summary
- Queued Signals Parameter Summary
- Real-Time Priority Parameter Summary
- Terminal Parameter Summary
- Maximum Users Parameter Summary
- Web Server Parameter Summary
- Miscellaneous Parameter Summary
- A Table of Tunable Kernel Parameters
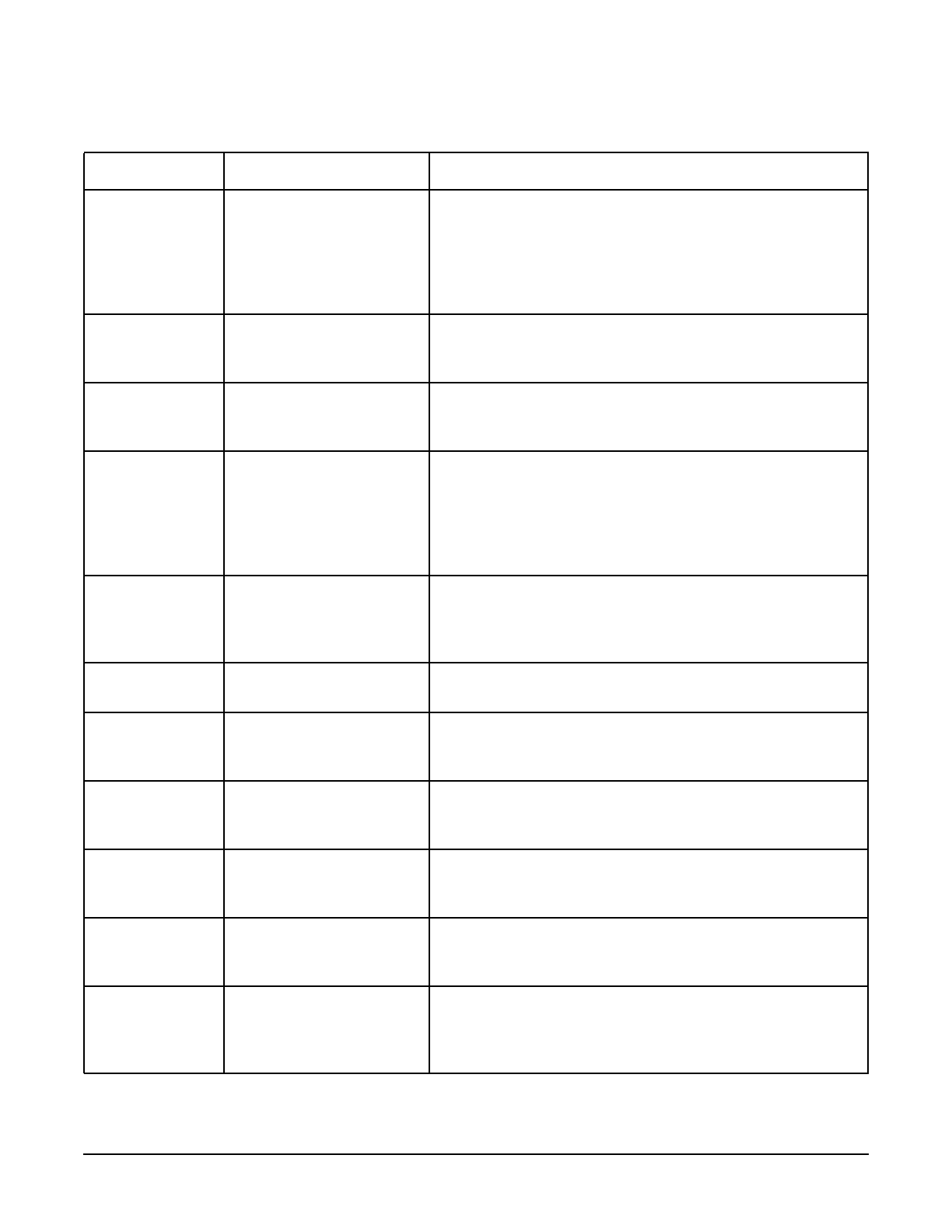
Table of Tunable Kernel Parameters
Appendix A
71
Streams NSTREVENT Maximum number of outstanding streams bufcalls that
are allowed to exist at any given time on the system. This
number should be equal to or greater than the maximum
bufcalls that can be generated by the combined total
modules pushed onto any given stream, and serves to limit
run-away bufcalls. Manpage: nstrevent (5).
Miscellaneous:
Terminal
nstrpty System-wide maximum number of streams-based
pseudo-ttys that are allowed on the system. Manpage:
nstrpty (5).
Streams nstrpty System-wide maximum number of streams-based
pseudo-ttys that are allowed on the system. Manpage:
nstrpty (5).
Streams NSTRPUSH Maximum number of streams modules that are allowed to
exist in any single stream at any one time on the system.
This provides a mechanism for preventing a software
defect from attempting to push too many modules onto a
stream, but it is not intended as adequate protection
against malicious use of streams. Manpage: nstrpush (5).
Streams NSTRSCHED Maximum number of streams scheduler daemons that are
allowed to run at any given time on the system. This value
is related to the number of processors installed in the
system. Manpage: nstrsched (5).
Miscellaneous:
Terminal
nstrtel Number of telnet session device files that are available on
the system. Manpage: nstrtel (5).
Memory Paging nswapdev Maximum number of devices, system-wide, that can be
used for device swap. Set to match actual system
configuration. Manpage: nswapdev (5).
Memory Paging nswapfs Maximum number of mounted file systems, system-wide,
that can be used for file system swap. Set to match actual
system configuration. Manpage: nswapfs (5).
Miscellaneous:
Memory
nsysmap Number of entries in the kernel dynamic memory virtual
address space resource map (32-bit processes). Manpage:
nsysmap (5).
Miscellaneous:
Memory
nsysmap64 Number of entries in the kernel dynamic memory virtual
address space resource map (64-bit processes). Manpage:
nsysmap (5).
Miscellaneous:
Disk I/O
o_sync_is_o_dsync Specifies whether an open() or fcntl() with the O_SYNC
flag set can be converted to the same call with the O_DSYNC
flag instead. This controls whether the function can return
before updating the file access. NO MANPAGE.
Table A-1 Tunable Kernel Parameters in Alphabetic Order (Continued)
Category Tunable Description










