Installing and Administering LAN/9000 Software
86 Chapter4
Troubleshooting LAN/9000
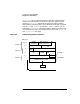
Diagnostic Flowcharts
Flowchart 2 Procedures
A. Execute: ifconfig <interface>. Execute ifconfig on the
interface you want to test. For example, to check LAN
interface lan0, enter:
ifconfig lan0
B. ifconfig successful? ifconfig is successful if the output
shows the correct Internet address and the flags,
typically: UP,BROADCAST,RUNNING.
C. Any error message returned? If ifconfig is not
successful, and an error message appears, go to
Flowchart 3. Flowchart 3 shows common error
messages and what to do for each.
D. Correct ifconfig flag settings. If ifconfig returns an
incorrect flag setting, re-execute the command with the
proper setting. For more information, refer to the
ifconfig(1M) man page. Start again with Flowchart
2, as necessary.
E. Execute: netstat -i. If ifconfig is successful, you know
the network interface has been configured correctly.
Using netstat, you can return statistics which show
the interface is operational. Enter:
netstat -in
netstat statistics give a quick check of key operating
parameters. For instance, if the Opkts value does not
change after attempting the file transfer, packets are
not being transmitted. Similarly, if the Ipkts value
does not change, packets are either not being received
by the local node or are not being sent by the remote
node, which may not be receiving your transmissions.
F. Interface name correct? Verify that the name for your
interface is what you expect. See the ifconfig(1M)
man page.
G. Correct encapsulation using ifconfig. Use the ifconfig
command to correct the encapsulation method of your
interface. For more information, refer to the
ifconfig(1M) man page. Go to E.
H. Suspect LAN card I/O problems? If the statistics