HP-UX System Administrator's Guide: Security Management HP-UX 11i v3 (B3921-90020, September 2010)
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX System Administrator's Guide: Security Management
- Table of Contents
- About this Document
- Part I Protecting Systems
- 1 Installing the HP-UX Operating Environment Securely
- 1.1 Installation Security Considerations
- 1.2 Preventing Security Breaches During the Boot Process
- 1.3 Enable Login Security for root
- 1.4 Using Boot Authentication to Prevent Unauthorized Access
- 1.5 Setting Install-Time Security Options
- 1.6 Installing Security Patches
- 1.7 Postinstallation Security Tips for Backup and Recovery
- 2 Administering User and System Security
- 2.1 Managing User Access
- 2.2 Authenticating Users During Login
- 2.3 Authenticating Users with PAM
- 2.4 Managing Passwords
- 2.4.1 System Administrator Responsibilities
- 2.4.2 User Responsibilities
- 2.4.3 Criteria of a Good Password
- 2.4.4 Changing the /etc/passwd Password File
- 2.4.5 The /etc/shadow Shadow Password File
- 2.4.6 Eliminating Pseudo-Accounts and Protecting Key Subsystems in /etc/passwd
- 2.4.7 Secure Login with HP-UX Secure Shell
- 2.4.8 Securing Passwords Stored in NIS
- 2.4.9 Securing Passwords Stored in LDAP Directory Server
- 2.5 Defining System Security Attributes
- 2.6 Handling setuid and setgid Programs
- 2.7 Preventing Stack Buffer Overflow Attacks
- 2.8 Protecting Unattended Terminals and Workstations
- 2.9 Protecting Against System Access by Remote Devices
- 2.10 Securing Login Banners
- 2.11 Protecting the root Account
- 3 HP-UX Standard Mode Security Extensions
- 4 Remote Access Security Administration
- 4.1 Overview of Internet Services and Remote Access Services
- 4.2 The inetd Daemon
- 4.3 Protection Against Spoofing with TCP Wrappers
- 4.4 Secure Internet Services
- 4.5 Controlling an Administrative Domain
- 4.6 Securing Remote Sessions Using HP-UX Secure Shell (SSH)
- 4.6.1 Key Security Features of HP-UX Secure Shell
- 4.6.2 Software Components of HP-UX Secure Shell
- 4.6.3 Running HP-UX Secure Shell
- 4.6.4 HP-UX Secure Shell Privilege Separation
- 4.6.5 HP-UX Secure Shell Authentication
- 4.6.6 Communication Protocols
- 4.6.7 HP-UX Secure Shell and the HP-UX System
- 4.6.8 Associated Technologies
- 4.6.9 Strong Random Number Generator Requirement
- 4.6.10 TCP Wrappers Support
- 4.6.11 chroot Directory Jail
- 1 Installing the HP-UX Operating Environment Securely
- Part II Protecting Data
- 5 File System Security
- 5.1 Controlling File Access
- 5.2 Setting Access Control Lists
- 5.3 Using HFS ACLs
- 5.4 Using JFS ACLs
- 5.4.1 Definition of a JFS ACL
- 5.4.2 How the System Generates a JFS ACL
- 5.4.3 Minimal JFS ACL
- 5.4.4 Additional JFS ACL user and group Entries
- 5.4.5 JFS ACL group and class Entries
- 5.4.6 Using the setacl and getacl Commands
- 5.4.7 Effect of chmod on class Entries
- 5.4.8 Example of Changing a Minimal JFS ACL
- 5.4.9 Default JFS ACLs
- 5.4.10 Changing JFS ACL with the setacl Command
- 5.5 Comparison of JFS and HFS ACLs
- 5.6 ACLs and NFS
- 5.7 Security Considerations for /dev Device Special Files
- 5.8 Protecting Disk Partitions and Logical Volumes
- 5.9 Security Guidelines for Mounting and Unmounting File Systems
- 5.10 Controlling File Security on a Network
- 6 Compartments
- 7 Fine-Grained Privileges
- 5 File System Security
- Part III Protecting Identity
- 8 HP-UX Role-Based Access Control
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Access Control Basics
- 8.3 HP-UX RBAC Components
- 8.4 Planning the HP-UX RBAC Deployment
- 8.5 Configuring HP-UX RBAC
- 8.6 Using HP-UX RBAC
- 8.7 Troubleshooting HP-UX RBAC
- 9 Audit Administration
- 8 HP-UX Role-Based Access Control
- A Trusted Systems
- B Other Security Products
- B.1 HP-UX AAA Server (RADIUS)
- B.2 HP-UX Bastille
- B.3 HP-UX Directory Server
- B.4 HP-UX Encrypted Volume and File System (EVFS)
- B.5 HP-UX HIDS
- B.6 HP-UX IPFilter
- B.7 HP-UX IPSec
- B.8 HP-UX LDAP-UX Integration
- B.9 HP-UX Secure Resource Partitions (SRP)
- B.10 HP-UX Secure Shell
- B.11 HP-UX Trusted Computing Services
- B.12 Security Patches
- Glossary
- Index
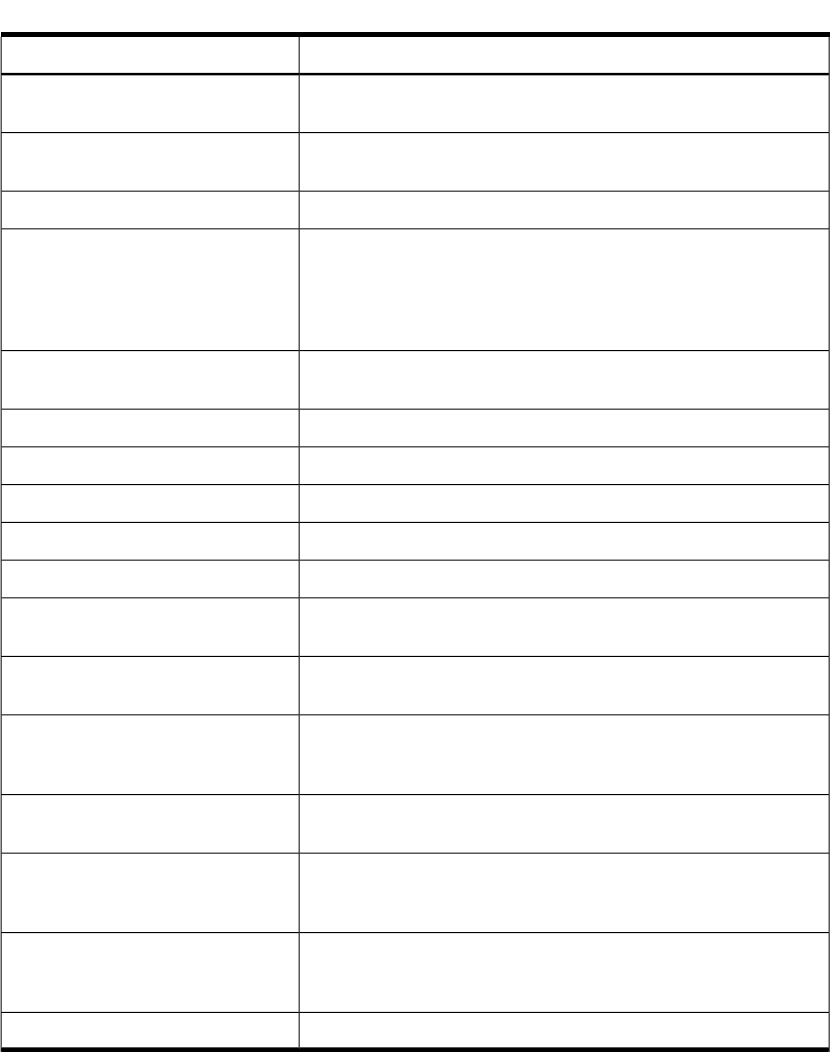
Table 7-3 Available Privileges (continued)
DescriptionPrivilege
Allows a process to bind to a privileged port. By default, port
numbers 0-1023 are privileged ports.
PRIV_NETPRIVPORT
Allows a process to configure an interface to listen in promiscuous
mode.
PRIV_NETPROMISCUOUS
Allows a process to access the raw internet network protocols.
PRIV_NETRAWACCESS
Allows a process to set the suid or sgid bits on any file if the
process has the OWNER privilege. It also allows a process to
change the ownership of a file without clearing the suid or sgid
bits, provided that the process is allowed to change the ownership
of the file.
PRIV_OBJSUID
Allows a process to override all restrictions with respect to UID
matching the owner of the file or resource.
PRIV_OWNER
Allows a process to change the system pset configuration.PRIV_PSET
Allows a process to perform reboot operations.
PRIV_REBOOT
Allows a process to access the rtprio() system call.PRIV_RTPRIO
Allows a process to control RTE psets.
PRIV_RTPSET
Allows a process to set POSIX.4 real-time priorities.
PRIV_RTSCHED
Allows a process to add and modify compartment rules on the
system.
PRIV_RULESCONFIG
Allows a process to generate auditing records for itself using
audwrite() system call.
PRIV_SELFAUDIT
Allows a process to use the serialize() system call force a target
process to run serially with other processes marked for
serialization.
PRIV_SERIALIZE
Allows a process to do certain administrative operations in the
Instant Capacity product.
PRIV_SPUCTL
Allows a process to manage system attributes, including the setting
of tunables, modifying the host name, domain name, and user
quotas.
PRIV_SYSATTR
Allows a process to perform NFS operations like exporting a file
system, the getfh() system call, NFS file locking, revoking NFS
authentication, and creating an NFS kernel daemon thread.
PRIV_SYSNFS
Allows a process to log trial mode information to the syslog file.
PRIV_TRIALMODE
130 Fine-Grained Privileges










