HP-UX System Administrator's Guide: Security Management HP-UX 11i v3 (B3921-90020, September 2010)
Table Of Contents
- HP-UX System Administrator's Guide: Security Management
- Table of Contents
- About this Document
- Part I Protecting Systems
- 1 Installing the HP-UX Operating Environment Securely
- 1.1 Installation Security Considerations
- 1.2 Preventing Security Breaches During the Boot Process
- 1.3 Enable Login Security for root
- 1.4 Using Boot Authentication to Prevent Unauthorized Access
- 1.5 Setting Install-Time Security Options
- 1.6 Installing Security Patches
- 1.7 Postinstallation Security Tips for Backup and Recovery
- 2 Administering User and System Security
- 2.1 Managing User Access
- 2.2 Authenticating Users During Login
- 2.3 Authenticating Users with PAM
- 2.4 Managing Passwords
- 2.4.1 System Administrator Responsibilities
- 2.4.2 User Responsibilities
- 2.4.3 Criteria of a Good Password
- 2.4.4 Changing the /etc/passwd Password File
- 2.4.5 The /etc/shadow Shadow Password File
- 2.4.6 Eliminating Pseudo-Accounts and Protecting Key Subsystems in /etc/passwd
- 2.4.7 Secure Login with HP-UX Secure Shell
- 2.4.8 Securing Passwords Stored in NIS
- 2.4.9 Securing Passwords Stored in LDAP Directory Server
- 2.5 Defining System Security Attributes
- 2.6 Handling setuid and setgid Programs
- 2.7 Preventing Stack Buffer Overflow Attacks
- 2.8 Protecting Unattended Terminals and Workstations
- 2.9 Protecting Against System Access by Remote Devices
- 2.10 Securing Login Banners
- 2.11 Protecting the root Account
- 3 HP-UX Standard Mode Security Extensions
- 4 Remote Access Security Administration
- 4.1 Overview of Internet Services and Remote Access Services
- 4.2 The inetd Daemon
- 4.3 Protection Against Spoofing with TCP Wrappers
- 4.4 Secure Internet Services
- 4.5 Controlling an Administrative Domain
- 4.6 Securing Remote Sessions Using HP-UX Secure Shell (SSH)
- 4.6.1 Key Security Features of HP-UX Secure Shell
- 4.6.2 Software Components of HP-UX Secure Shell
- 4.6.3 Running HP-UX Secure Shell
- 4.6.4 HP-UX Secure Shell Privilege Separation
- 4.6.5 HP-UX Secure Shell Authentication
- 4.6.6 Communication Protocols
- 4.6.7 HP-UX Secure Shell and the HP-UX System
- 4.6.8 Associated Technologies
- 4.6.9 Strong Random Number Generator Requirement
- 4.6.10 TCP Wrappers Support
- 4.6.11 chroot Directory Jail
- 1 Installing the HP-UX Operating Environment Securely
- Part II Protecting Data
- 5 File System Security
- 5.1 Controlling File Access
- 5.2 Setting Access Control Lists
- 5.3 Using HFS ACLs
- 5.4 Using JFS ACLs
- 5.4.1 Definition of a JFS ACL
- 5.4.2 How the System Generates a JFS ACL
- 5.4.3 Minimal JFS ACL
- 5.4.4 Additional JFS ACL user and group Entries
- 5.4.5 JFS ACL group and class Entries
- 5.4.6 Using the setacl and getacl Commands
- 5.4.7 Effect of chmod on class Entries
- 5.4.8 Example of Changing a Minimal JFS ACL
- 5.4.9 Default JFS ACLs
- 5.4.10 Changing JFS ACL with the setacl Command
- 5.5 Comparison of JFS and HFS ACLs
- 5.6 ACLs and NFS
- 5.7 Security Considerations for /dev Device Special Files
- 5.8 Protecting Disk Partitions and Logical Volumes
- 5.9 Security Guidelines for Mounting and Unmounting File Systems
- 5.10 Controlling File Security on a Network
- 6 Compartments
- 7 Fine-Grained Privileges
- 5 File System Security
- Part III Protecting Identity
- 8 HP-UX Role-Based Access Control
- 8.1 Overview
- 8.2 Access Control Basics
- 8.3 HP-UX RBAC Components
- 8.4 Planning the HP-UX RBAC Deployment
- 8.5 Configuring HP-UX RBAC
- 8.6 Using HP-UX RBAC
- 8.7 Troubleshooting HP-UX RBAC
- 9 Audit Administration
- 8 HP-UX Role-Based Access Control
- A Trusted Systems
- B Other Security Products
- B.1 HP-UX AAA Server (RADIUS)
- B.2 HP-UX Bastille
- B.3 HP-UX Directory Server
- B.4 HP-UX Encrypted Volume and File System (EVFS)
- B.5 HP-UX HIDS
- B.6 HP-UX IPFilter
- B.7 HP-UX IPSec
- B.8 HP-UX LDAP-UX Integration
- B.9 HP-UX Secure Resource Partitions (SRP)
- B.10 HP-UX Secure Shell
- B.11 HP-UX Trusted Computing Services
- B.12 Security Patches
- Glossary
- Index
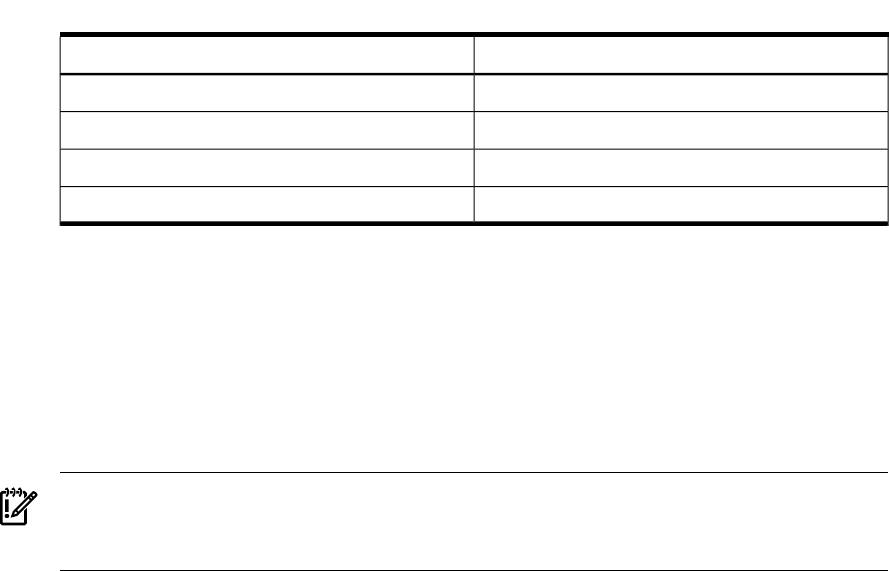
Table 5-5 HFS and JFS ACL Equivalents (continued)
JFS EquivalentHFS Name
—none—setaclentry(3C)
—none—strtoacl(3C)
aclsort(3C)—none—
aclv(5)acl(5)
5.6 ACLs and NFS
The Network File System (NFS) has no facility to pass ACL information about remote
files. Therefore, ACLs are not visible on remote files by NFS. The ls -l command
will not show that ACLs exist on a remote file, but the ACL control over access
permissions remains effective.
Individual manpage entries specify the behavior of the various system calls, library
calls, and commands under these circumstances.
IMPORTANT: Use caution when transferring a file with optional entries over a network,
or when manipulating a remote file, because NFS can delete optional entries with no
notification.
5.7 Security Considerations for /dev Device Special Files
Access to all devices in the system is controlled by device special files, which enable
programs to be device independent. These files are shipped with permission settings
that enable proper use and maximum security.
If you install any other device special files, see insf(1M) for information about correct
permission settings.
Because device special files can be as vulnerable to tampering as any other file, observe
the following precautions:
• Keep all device special files in the /dev directory.
• Protect the memory files, /dev/mem and /dev/kmem, from casual access, because
these files contain sensitive user information. For example, a program that watches
memory for an invocation of the login program might copy the password from
the login program buffers when a user types it in. The file protections should be
set to:
crw-r----- 1 bin sys 3 0x000001 Jun 9 2006 /dev/kmem
crw-r----- 1 bin sys 3 0x000000 Jun 9 2006 /dev/mem
• Protect all disk special files:
5.6 ACLs and NFS 103










