HP StorageWorks Virtual Array 7000 Family User and Service Guide (January 2005)
Table Of Contents
- Warranty Information
- Product Overview
- System Configurations
- Lowest Entry Point, Non-HA Minimum Configuration (VA 7100 only)
- Lowest Entry Point, Non-HA Minimum Configuration (VA 7410)
- Entry Level Non-Cluster With Path Redundancy (All VA arrays)
- Entry Level Cluster with Path Redundancy High Availability (VA 7410)
- Midrange Non-Cluster (All VA arrays)
- Midrange Non-Cluster (VA 7410)
- Midrange Non-Cluster with Full Storage Path Redundancy (All VA Arrays)
- Typical Non-Clustered with Path Redundancy (VA 7410)
- Typical Clustered Configuration (All VA models)
- Typical Clustered Configuration (VA 7410)
- HP-UX MC Service Guard or Windows 2000 Cluster (All VA arrays)
- Highly Redundant Cluster (VA 7410)
- Typical Highly Redundant Cluster (All VA models)
- Typical Highly Redundant Cluster (VA 7410)
- Troubleshooting
- Servicing & Upgrading
- Specifications & Regulatory Statements
48 Product Overview
Upon completion of the rebuild of a failed disk, the array is once again
protected against any single disk failure.
Note RAID groups with an even number of disks will always have a
single adjacent disk after a disk failure, and RAID groups with
an odd number of disks will always have two adjacent disks
after a disks failure.
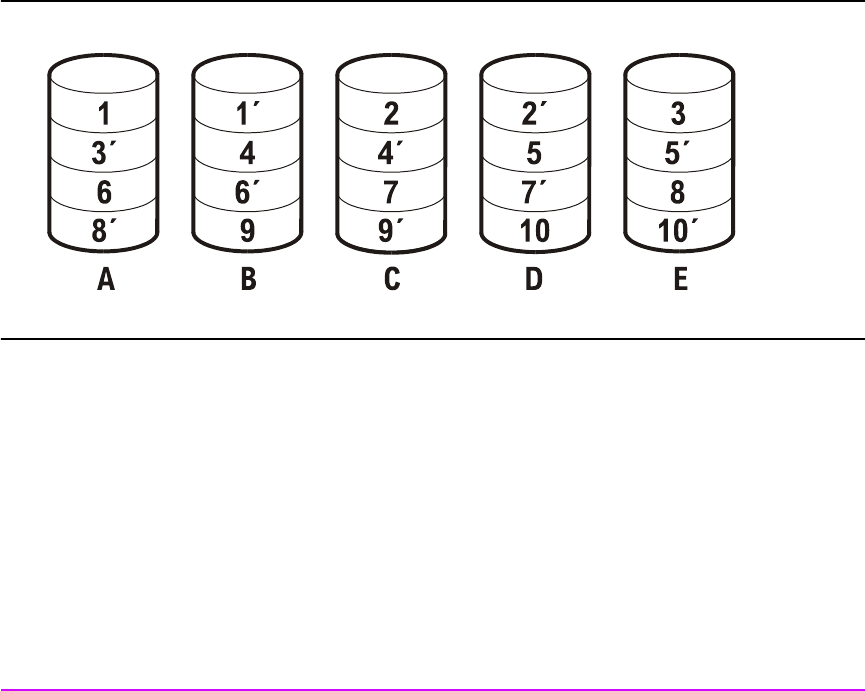
The segment size for a Virtual Array is always 256 Kbytes.
The Virtual Array technology and RAID 1+0 stripes distribute data to all the
disks in an RG, thus effectively eliminating ‘hot spots’ — disks that are
accessed so frequently that they impede the performance of the array.
Figure 18 RAID 1+0 Data Storage Example
RAID 5DP
RAID 5DP provides data redundancy and improves cost-efficiency by using a
more efficient method of storing the redundancy data. Although virtual array
technology attempts to minimize any performance impact, there can be a
performance penalty associated with write operations. This can impact system
performance when using applications that frequently update large quantities of
data (greater than 10% of a fully allocated array), or performs predominantly
small (<256 Kbytes) random write operations.
RAID 5DP uses two algorithms to create two independent sets of redundancy
data. This allows the array to reconstruct RAID 5DP data in the event of two










