HP StorageWorks Virtual Array 7000 Family User and Service Guide (January 2005)
Table Of Contents
- Warranty Information
- Product Overview
- System Configurations
- Lowest Entry Point, Non-HA Minimum Configuration (VA 7100 only)
- Lowest Entry Point, Non-HA Minimum Configuration (VA 7410)
- Entry Level Non-Cluster With Path Redundancy (All VA arrays)
- Entry Level Cluster with Path Redundancy High Availability (VA 7410)
- Midrange Non-Cluster (All VA arrays)
- Midrange Non-Cluster (VA 7410)
- Midrange Non-Cluster with Full Storage Path Redundancy (All VA Arrays)
- Typical Non-Clustered with Path Redundancy (VA 7410)
- Typical Clustered Configuration (All VA models)
- Typical Clustered Configuration (VA 7410)
- HP-UX MC Service Guard or Windows 2000 Cluster (All VA arrays)
- Highly Redundant Cluster (VA 7410)
- Typical Highly Redundant Cluster (All VA models)
- Typical Highly Redundant Cluster (VA 7410)
- Troubleshooting
- Servicing & Upgrading
- Specifications & Regulatory Statements
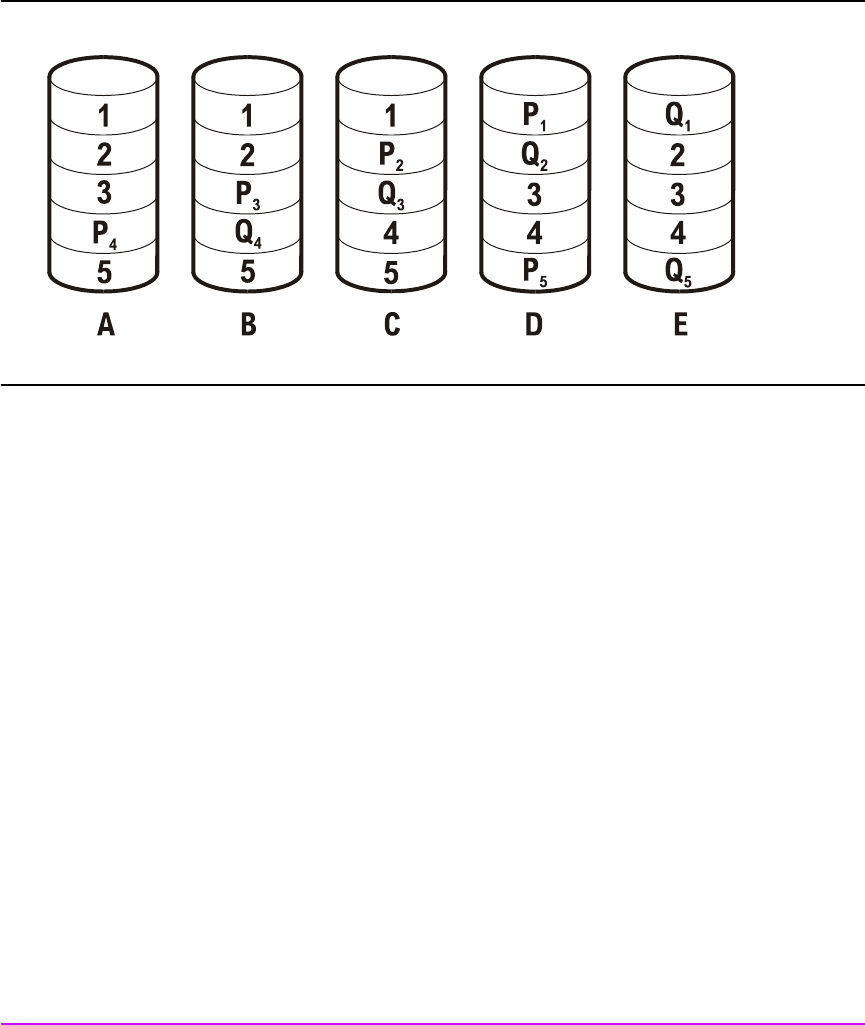
50 Product Overview
Figure 19 RAID 5DP Data Storage Example
Data Availability and AutoRAID
When configured in the AutoRAID mode, the Virtual Array uses a combination
of RAID 1+0 and RAID 5DP. As a result, the disks within a single RG can have
a portion of its data capacity used as RAID 1+0, while the other portion is
used as RAID 5DP.
During disk failures, rebuild is directed to rebuild the most statistically
vulnerable data first. After the first disk failure in an RG, the rebuild process
prioritizes RAID 1+0 data first. If a second disk fails before the rebuild
completes, then RAID 5DP is prioritized first. This logic represents the statistical
availability model for the two failure states. Once the RAID 1+0 data has
been rebuilt, the RAID group is protected against any two simultaneous disk
failures. The status of a RAID 1+0 data rebuild can be displayed using
Command View.
AutoRAID and Dynamic Data Migration
Unlike conventional disk array, the virtual array has the option to self manage
the RAID level selection based on the workload characteristics. In this mode,
the array controller attempts to place data in the RAID level that provides the
best performance based on how the host accesses that data. This RAID level
selection is both automatic and dynamic. Dynamic Data Migration is a
background operation, and gives priority to host operations. It is possible that










