3.7.0 HP StorageWorks HP Scalable NAS File Serving Software provisioning guide for Oracle HP Scalable NAS (AG513-96013, October 2009)
Virtual NFS Server RPC reply cache
The NFS protocol allows requests to be resent. Some requests such as write, create,
remove, rename, link, unlink, and so forth must be executed on the server once and
only once. These operations are called non-idempotent. The NFS server must keep
a cache of its current non-idempotent requests to ensure that it does not repeat a
request should another identical request arrive. This cache is called the RPC reply
cache.
Without an RPC reply cache, NFS clients that retry non-idempotent operations whose
success invalidates their pre-conditions may see erroneous error returns. The
conventional reply cache prevents this problem. It is kept in memory on each node,
with no provision to transfer it between nodes or save and restore it. With the addition
of virtualized NFS servers that can move between nodes, clients are potentially again
exposed to spurious error returns when a VNFS service transitions to another node.
However, FS Option for Linux provides a virtualized NFSD RPC reply cache feature,
which allows the state of the NFSD RPC reply cache to be associated with the relevant
virtualized NFS server (VNFS host). It is transferred together with the virtualized NFS
server when a transition occurs to another host. It is recommended that this feature,
which is disabled by default, be activated when using Oracle over NFS. See
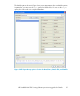
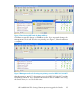
“Virtualized NFSD RPC reply caches” in the HP Scalable NAS File Serving Software
administration guide for activation details.
Special instructions for Oracle Home
As described in the next section, Oracle uses file locking at instance startup when
not running Real Application Clusters. On NFS, this requires NFS Server support for
the NLM locking protocol. Again, for non-RAC databases it is critical that the filesystem
containing ORACLE_HOME possess the following characteristics:
• Single Virtual NFS Service Association. It is imperative that the ORACLE_HOME
filesystem be presented through a single Virtual NFS Service.
• FS Option for Linux must be configured to enable NLM.
PSFS filesystems can be serviced (exported) by multiple Virtual NFS Services (many
virtual IP addresses) simultaneously. However, if the ORACLE_HOME filesystem is
exported through multiple Virtual NFS Services, a race condition is possible during
VNFS rehosting or failover where an instance startup can be incorrectly granted a
lock on the $ORACLE_HOME/dbs/lk<DBNAME> file. If ORACLE_HOME is presented
through a single VNFS, this problem will not occur. HP recommends this approach.
Presenting ORACLE_HOME through a single Virtual NFS Service will limit I/O
bandwidth to a single NAS head. This is not an issue as the I/O load on
NAS Administrator: deploying HP Scalable NAS for use with Oracle26