3.7.0 HP StorageWorks HP Scalable NAS File Serving Software provisioning guide for Oracle HP Scalable NAS (AG513-96013, October 2009)
Managing Virtual NFS Services
Before NFS mounting the storage on the NFS client, the NAS administrator must
configure the Virtual NFS Service that the Oracle server (NFS client) will use to access
the storage. If you are using DNS, the appropriate Virtual IP addresses and host
names need to be assigned beforehand. It is a good idea to first verify that the host
name you plan to use resolves. Do this by attempting to ping the host name, which
should show the resolved IP address. Until the Virtual NFS service is created, the
ping will not actually respond. For example, if the host name will be
voraclehome.customer.com, you can run the ping and see that it is resolving to
192.168.60.71, as expected.
# ping voraclehome.customer.com
PING voraclehome.customer.com (192.168.60.71) 56(84) bytes of data.
From voraclehome.customer.com (192.168.60.71) icmp_seq=1 Destination Host
Unreachable ….
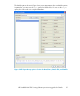
Figure 4 shows the HP Scalable NAS Management Console with an example of
associating an Export Group with both a Virtual NFS Service and the NAS heads
that will act as the primary and 1st backup in the event of a NAS head failure. The
example shows that:
• The Virtual NFS Service will be created with IP address 192.168.60.71, which
is what DNS will resolve for voraclehome.customer.com.
• The Export Group that will be presented through the Virtual NFS Service will be
called “OracleHome.”
• NAS servers (heads) for this VNFS are tmr6s18.customer.com as the primary and
tmr6s17.customer.com as the 1st backup. Two other NAS servers are available
but are currently not supporting this Virtual NFS Service.
• Because /u03/app/oracle was previously added to this Export Group (see
Figure 3), storage can be accessed via mounts using either the IP address
(192.168.60.71) or the virtual host name, voraclehome.customer.com.
NAS Administrator: deploying HP Scalable NAS for use with Oracle22