3.7.0 HP StorageWorks HP Scalable NAS File Serving Software administration guide - HP Scalable NAS 3.7 for Linux (AG513-96002, October 2009)
is equal to or greater than the backup node where the Virtual NFS Service currently
resides, the Virtual NFS Service will automatically attempt to fail over to that node.
• NOFAILBACK. This policy is intended to minimize failovers. The Virtual NFS Service
remains active on the backup node, even after the primary node is returned to
service, until a “healthier” node becomes available, at which point the Virtual
NFS Service fails over to that node. (On a “healthier” node, more of the services
associated with the Virtual NFS Service will be up than on the node currently
hosting the Virtual NFS Service.)
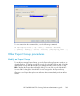
Network Interfaces Available/Configured: Move the interfaces on which the Virtual
NFS Service should be configured from the Available column to the Configured
column. The first interface that you select is the primary interface. The other interfaces
that you select are backups. You can use the up and down arrows to reorder the
interfaces on the Configured column.
The Virtual NFS Service appears on the Servers, Virtual Hosts, and Applications tabs
on the Management Console. Following is the Virtual Hosts view.
To create a Virtual NFS Service from the command line, use this command:
mx vnfs add [--exportgroup <exportgroup_name>|NONE] [--policy
autofailback|nofailback] [--activitytype single|always] <vnfs>
<network_interface> ...
You can view the configuration and status of Virtual NFS Services and the Export
Groups associated with them on the Management Console. See High-availability
monitors, page 175 and also Application states, page 277.
To view Virtual NFS Services from the command line, use this command:
mx vnfs status [--up|--down] [--enabled|--disabled]
[--primary|--backup] [--active|--inactive] [<vnfs> ...]
HP Scalable NAS File Serving Software administration guide 189