Serial Attached SCSI technologies and architectures, 4th edition
8
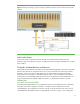
Figure 6: External port topology to support cascading an additional enclosure and connecting both ports to the
enclosure
Multi-node clusters
A multi-node cluster using SAS provides an alternative to clustered Fibre Channel local loop
topologies. This SAS architecture can give you high performance and high availability with no single
point of failure.
Dual-path and dual-domain architectures
The International Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS) T10 Technical Committee
defines a SCSI domain as ―the interconnection of two or more SCSI devices and a service delivery
subsystem.‖ When any part of the data pathway in the single domain fails, data transfer stops
because there is no secondary, or redundant, pathway. But you can use dual-path or dual-domain
architectures to create redundant pathways from servers to storage devices. These architectures use
single- and dual-ported serial HDDs and dual controllers, or dual-ported controllers, to provide
redundant paths.
Dual-path with cascaded JBODs
Dual-path SATA implementations use a single-domain method of providing tolerance to cable failure.
Dual paths can prevent a single point of failure in complex enterprise configurations such as
cascaded JBODs. This configuration connects a controller to the IO module at each end of a set of
cascaded JBODs. Each JBOD contains a single expander, as shown in Figure 7. This configuration