Managing Serviceguard 11th Edition, Version A.11.16, Second Printing June 2004
Understanding Serviceguard Software Components
How Package Control Scripts Work
Chapter 392
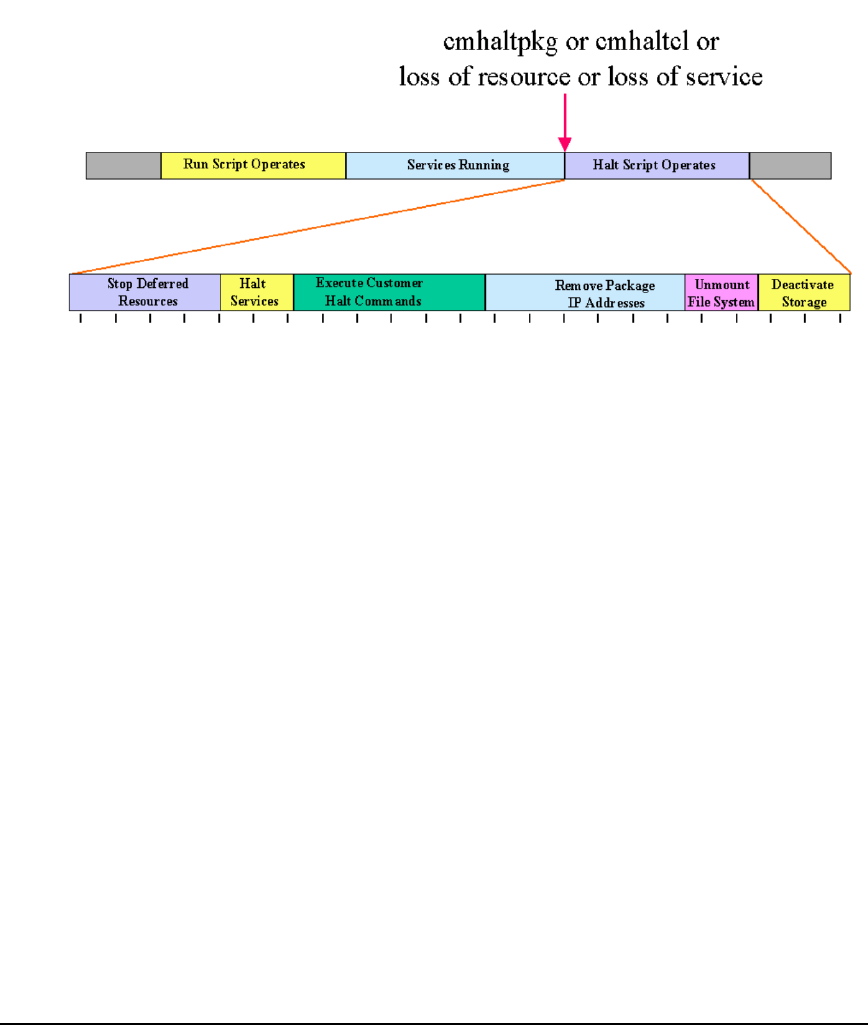
Figure 3-15 Package Time Line for Halt Script Execution
At any step along the way, an error will result in the script exiting
abnormally (with an exit code of 1). Also, if the halt script execution is
not complete before the time specified in the HALT_SCRIPT_TIMEOUT, the
package manager will kill the script. During halt script execution,
messages are written to a log file in the same directory as the halt script.
This log has the same name as the halt script and the extension.log.
Normal starts are recorded in the log, together with error messages or
warnings related to halting the package.
Normal and Abnormal Exits from the Halt Script
The package’s ability to move to other nodes is affected by the exit
conditions on leaving the halt script. The following are the possible exit
codes:
• 0—normal exit. The package halted normally, so all services are
down on this node.
• 1—abnormal exit, also known as NO_RESTART exit. The package did
not halt normally. Services are killed, and the package is disabled
globally. It is not disabled on the current node, however.
• Timeout—Another type of exit occurs when the
HALT_SCRIPT_TIMEOUT is exceeded. In this scenario, the package is
killed and disabled globally. It is not disabled on the current node,
however.










