Serviceguard NFS Toolkit A.11.11.06, A.11.23.05 and A.11.31.05 Administrator's Guide HP-UX 11i v1, v2, and v3
Table Of Contents
- Serviceguard NFS Toolkit A.11.11.06, A.11.23.05 and A.11.31.05 Administrator's Guide
- Table of Contents
- 1 Overview of Serviceguard NFS
- Limitations of Serviceguard NFS
- Overview of Serviceguard NFS Toolkit A.11.31.05 with Serviceguard A.11.18 (or later) and Veritas Cluster File System Support
- Overview of the Serviceguard NFS Modular Package
- Overview of the NFS File Lock Migration Feature
- Overview of NFSv4 File Lock Migration Feature
- Overview of Serviceguard NFS with Serviceguard A.11.17 Support
- Integrating Support for Cluster File Systems into Serviceguard NFS Toolkit
- Overview of Cluster File Systems in Serviceguard NFS Toolkit
- Limitations and Issues with the current CFS implementation
- Supported Configurations
- How the Control and Monitor Scripts Work
- 2 Installing and Configuring Serviceguard NFS Legacy Package
- Installing Serviceguard NFS Legacy Package
- Before Creating a Serviceguard NFS Legacy Package
- Configuring a Serviceguard NFS Legacy Package
- Copying the Template Files
- Editing the Control Script (nfs.cntl)
- Editing the NFS Control Script (hanfs.sh)
- Editing the File Lock Migration Script (nfs.flm)
- Editing the NFS Monitor Script (nfs.mon)
- Editing the Package Configuration File (nfs.conf)
- Configuring Server-to-Server Cross-Mounts (Optional)
- Creating the Cluster Configuration File and Bringing Up the Cluster
- Configuring Serviceguard NFS Legacy Package over CFS Packages
- 3 Installing and Configuring Serviceguard NFS Modular Package
- Installing Serviceguard NFS Modular Package
- Before Creating a Serviceguard NFS Modular Package
- Configuring a Serviceguard NFS Modular Package
- Configuring Serviceguard NFS Modular Package over CFS Packages
- 4 Migration of Serviceguard NFS Legacy Package to Serviceguard NFS Modular Package
- 5 Sample Configurations for Legacy Package
- Example One - Three-Server Mutual Takeover
- Example Two - One Adoptive Node for Two Packages with File Lock Migration
- Cluster Configuration File for Adoptive Node for Two Packages with File Lock Migration
- Package Configuration File for pkg01
- NFS Control Scripts for pkg01
- NFS File Lock Migration and Monitor Scripts for pkg01
- Package Configuration File for pkg02
- NFS Control Scripts for pkg02
- NFS File Lock Migration and Monitor Scripts for pkg02
- Example Three - Three-Server Cascading Failover
- Example Four - Two Servers with NFS Cross-Mounts
- 6 Sample Configurations for Modular Package
- Index
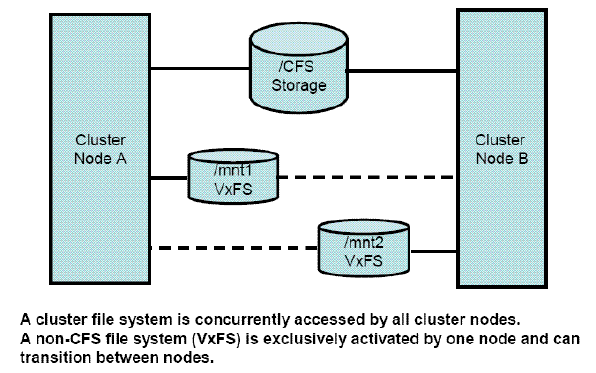
Figure 1-1 CFS versus Non-CFS (VxFS) Implementation
In a Serviceguard CFS environment, files and filesystems are concurrently accessible on multiple
nodes. When a package fails over, the adoptive systems do not have to mount the disks from the
failed system because they are already mounted. There is a new multi-node package that runs
on each server in the cluster and exports all the cluster filesystems. The exported filesystems do
not have to be reexported when a package fails over. These factors may reduce failover time.
The files and filesystems can be shared and accessed concurrently within the cluster. However,
file sharing and access from outside the cluster will still require NFS — client systems which are
not members of the CFS cluster will use NFS to access the shared filesystems.
Cross mounting (with nfs_xmnt script) is not needed since you can use CFS to share files and
filesystems within the cluster.
Figures 1–2 and 1–3 also show how files and filesystems are accessed differently in a CFS
environment versus a non-CFS environment. In a non-CFS environment, clients must access the
server which exports a specific filesystem. In a CFS environment, clients can access the cluster
via a load balancer or another mechanism such as a DNS round-robin scheme (represented by
the cloud in Figure 3.) Each NFS client can be directed to the server which currently has the most
capacity available. This approach has a limitation that clients are bound to a particular NFS server
when they issue the mount command.
14 Overview of Serviceguard NFS










