Using HP Serviceguard for Linux with VMware virtual machines - Technical white paper
13
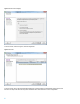
Figure 12. HP Serviceguard cluster of virtual machine guests on different physical nodes
A Serviceguard cluster consisting of VM guests on separate physical servers is shown in figure 12. In this configuration,
Serviceguard provides HA for applications against failures of physical nodes, VMware ESX hypervisor, VM guest, and
failure of application itself. A failed application can be restarted on the same virtual machine guest or failed over to
another virtual machine guest on a different physical node.
Data integrity during package failover
Virtual machines run on ESX server hypervisor. When a virtual machine dies, Serviceguard fails over the applications
running on the failed machine to another physical server or a virtual machine running on another machine. Serviceguard
maintains data integrity between the failed application and the new instance of it using persistent reservation of LUNs
shared between nodes of the cluster. Shared storage used in a cluster that includes VMware guests must support
persistent reservation.
Package parameter for a virtual machine cluster
Modular packages: All modular packages used in Serviceguard for Linux clusters that have at least one virtual machine
node must include the persistent_res module. This module contains the parameter sglx_vm, which you must set to on to
ensure data integrity during package failover. (By default it is off.)
Legacy packages: You need to modify the package control script to enable persistent reservation. In the package
control script, you will find a variable SGLX_VM, set to off by default. If any cluster node is a VMware guest, you must set
this variable to on for all packages.
For more information about modular and legacy packages, see the latest release notes of the HP Serviceguard for Linux,
which you can find at hp.com/go/linux-serviceguard-docs
→Getting started.