HP Serviceguard A.11.20.20 for Linux Release Notes, March 2014
For SUSE Linux Enterprise Server: /opt/cmcluster/conf/cmcluster.rc
e. Repeat this process for each node in the cluster.
NOTE: Be sure to plan sufficient system capacity to allow moving the packages from
node to node during the process without an unacceptable loss of performance. If the
cluster fails before the rolling upgrade is complete (because of a catastrophic power
failure, for example), you can restart it by entering the cmruncl command from a node
which has been upgraded to the latest revision of the software.
If the cluster fails before the rolling upgrade is complete (because of a catastrophic power failure,
for example), you can restart it by entering the cmruncl command from a node which has been
upgraded to the latest revision of the software.
6.11.1 Keeping Kernels consistent
If you change kernel parameters as a part of doing a rolling upgrade, be sure to make the same
changes on all nodes that can run the same packages.
6.11.2 Example
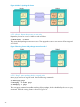
The following example shows a simple rolling upgrade on two nodes running one package each.
NOTE: This and the following figures are from a use case in which the starting point of the
upgrade was Serviceguard A.11.19 and Red Hat Enterprise Linux 5.7, and the rolling upgrade
was to Serviceguard A.11.20.00.
Figure 1 Running cluster before rolling upgrade
6.11.2.1 Step 1. Halt first node
Halt the first node, as follows
# cmhaltnode -f node1
This will cause Pkg1 to be halted cleanly and moved to node 2. The Serviceguard daemon on
node 1 is halted, and the result is shown in Figure 2.
24