HP Serviceguard Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit User Guide (5900-2145, April 2013)
Table Of Contents
- HP Serviceguard Enterprise Cluster Master Toolkit User Guide
- Contents
- 1 Introduction
- 2 Using the Oracle Toolkit in an HP Serviceguard Cluster
- Overview
- Supported Versions
- Support for Oracle Database Without ASM
- Supporting Oracle ASM Instance and Oracle Database with ASM
- What is Automatic Storage Management (ASM)?
- Why ASM over LVM?
- Configuring LVM Volume Groups for ASM Disk Groups
- Sample command sequence for configuring LVM Volume Groups
- Serviceguard support for ASM on HP-UX 11i v3 onwards
- Framework for ASM support with Serviceguard
- Installing, Configuring, and Troubleshooting
- Setting up DB instance and ASM instance
- Setting up the Toolkit
- ASM Package Configuration Example
- Modifying a Legacy Database Package Using an Older Version of Oracle ECMT Scripts to use the Scripts Provided for ASM Support
- Adding the Package to the Cluster
- Node-specific Configuration
- Error Handling
- Network Configuration
- Database Maintenance
- Configuring and packaging Oracle single-instance database to co-exist with SGeRAC packages
- Configuring Oracle single-instance database that uses ASM in a Coexistence Environment
- Attributes newly added to ECMT Oracle toolkit
- Configuring a modular failover package for an Oracle database using ASM in a coexistence environment
- Configuring a legacy failover package for an Oracle database using ASM in a Coexistence Environment
- ECMT Oracle Toolkit Maintenance Mode
- Supporting EBS database Tier
- Oracle ASM Support for EBS DB Tier
- 3 Using the Sybase ASE Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster on HP-UX
- Overview
- Sybase Information
- Setting up the Application
- Setting up the Toolkit
- Sybase Package Configuration Example
- Creating the Serviceguard package using Modular method
- Adding the Package to the Cluster
- Node-specific Configuration
- Error-Handling
- Network configuration
- Database Maintenance
- Cluster Verification for Sybase ASE Toolkit
- 4 Using the DB2 Database Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster in HP-UX
- 5 Using MySQL Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- MySQL Package Configuration Overview
- Setting Up the Database Server Application
- Setting up MySQL with the Toolkit
- Package Configuration File and Control Script
- Creating Serviceguard Package Using Modular Method
- Applying the Configuration and Running the Package
- Database Maintenance
- Guidelines to Start Using MySQL Toolkit
- 6 Using an Apache Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- 7 Using Tomcat Toolkit in a HP Serviceguard Cluster
- Tomcat Package Configuration Overview
- Multiple Tomcat Instances Configuration
- Configuring the Tomcat Server with Serviceguard
- Setting up the Package
- Creating Serviceguard Package Using Modular Method
- Setting up the Toolkit
- Error Handling
- Tomcat Server Maintenance
- Configuring Apache Web Server with Tomcat in a Single Package
- 8 Using SAMBA Toolkit in a Serviceguard Cluster
- 9 Using HP Serviceguard Toolkit for EnterpriseDB PPAS in an HP Serviceguard Cluster
- 10 Support and Other resources
- 11 Acronyms and Abbreviations
- Index
3. Copy the configuration file /etc/my.cnf to /MySQL_1/my.cnf.
4. Modify /MySQL_1/my.cnf to configure the DB for your unique environment. Changes may
include specific assignments to the following parameters:
[mysqld]
* datadir=/MySQL_1/mysql
* socket=/MySQL_1/mysql/mysql.sock
* port=<UNIQUE PORT NUMBER>
mysqld_safe]
* err-log=/MySQL_1/mysql/mysqld.err
* pid-file=/etc/cmcluster/pkg/mysql1/mysqld.pid
Multiple database instances can be configured in the environment using this method because each
database instance resides in its own filesystem.
Setting up MySQL with the Toolkit
Toolkit overview
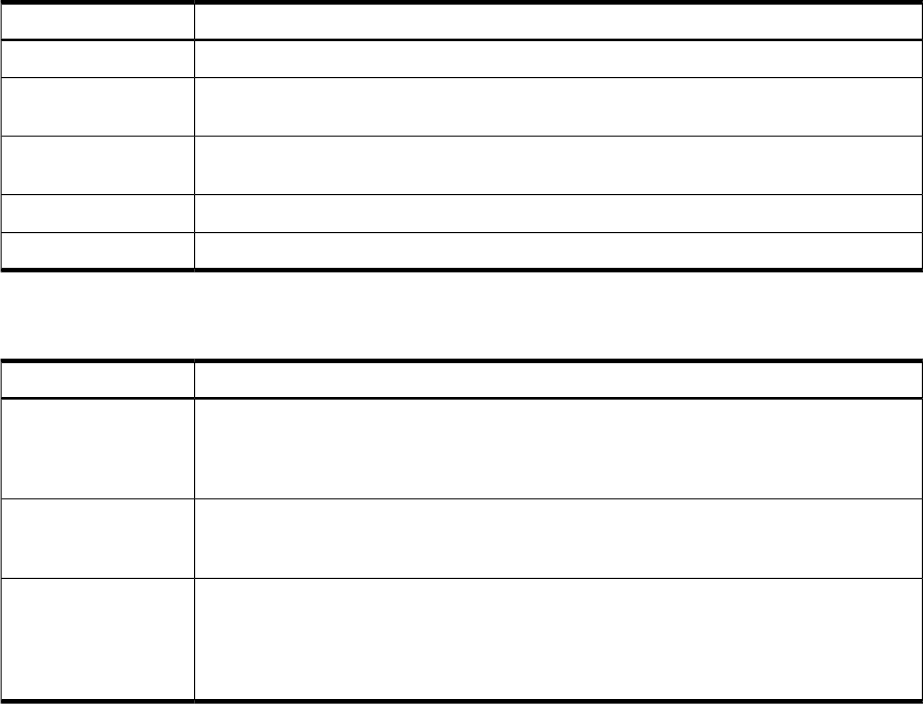
Table 15 (page 91) lists the files that are included in the toolkit for MySQL.
Table 15 Files in MySQL toolkit
DescriptionFile Name
The contents of the README file have been moved to this user guide.README
Toolkit Interface Script. This script interfaces between the Package Control Script and the
toolkit main script (hamysql.sh).
toolkit.sh
Toolkit Configuration File. This file contains a list of pre-defined variables that may be changed
for your unique environment.
hamysql.conf
Toolkit Main Script. Contains the internal functions that support start/stop of a MySQL instance.hamysql.sh
Toolkit Monitor Script. Contains the internal functions for monitoring a DB server instance.hamysql.mon
Table 16 (page 91) lists the files that are used only during the modular method of packaging.
Table 16 Scripts used in Modular Method of Packaging
DescriptionFile Name
For every parameter in the legacy toolkit user configuration file, there is an attribute in the
ADF. It also has an additional attribute TKIT_DIR which is analogous to the package directory
Attribute
Definition File
(mysql)
in the legacy method of packaging. The ADF is used to generate a package ASCII template
file.
This script is called by the Master Control Script and acts as an interface between the Master
Control Script and the Toolkit interface script (toolkit.sh). It is also responsible for calling the
Toolkit Configuration File Generator Script (see description below).
Module Script
(tkit_module.sh)
Toolkit Configuration File. This file contains a list of pre-defined variables that can be changed
for your unique environment.
Toolkit
Configuration
File Generator
Script
(tkit_gen.sh)
MySQL configuration file (my.cnf)
Table 18 lists the parameters that are included in the configuration file /etc/my.cnf. This file
must be copied to the file system on the shared storage ( for example, /etc/my.cnf will be
copied to /MySQL_1/my.conf). You must manually set each parameter with unique values for
each DB instance configured.
Setting up MySQL with the Toolkit 91










